1 引言
2021年8月9日,联合国评估气候变化相关科学的政府间气候变化专门委员会(Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, IPCC)发布了第六次评估报告(AR6)的政策制定者摘要(SPM),首次确认人类影响导致全球变暖是明确的[1]。国际社会普遍认为,二氧化碳过度排放是引起气候变化的主要因素。我国已明确表态和承诺,将采取更加有力的政策和措施,二氧化碳排放力争于2030年前达到峰值,努力争取2060年前实现碳中和。实现“双碳”目标不是要完全禁止二氧化碳排放,而是在降低二氧化碳排放的同时,促进二氧化碳吸收,用吸收抵消排放,这就需要以技术创新引领低碳发展新格局,二氧化碳捕集利用与封存(CCUS)技术是我国实现“双碳”目标的有益技术探索[2]。碳捕获、利用与封存(Carbon Capture,Utilization and Storage,CCUS)技术是实现减排目标过程中唯一一组既能直接减少关键领域碳排放,又能降低已有CO2浓度以平衡无法避免的碳排放的技术,是实现“净”零目标的关键部分[3]。可以说在化石燃料无法完全清退的情况下,CCUS技术的研发推广势在必行[4]。
CO2可以作为一系列产品和服务的原料。CO2的潜在应用包括直接使用(不发生化学变化),以及将CO2转化为其他产品(发生化学变化)。本研究重点关注CO2在化工转化利用方面的研究发展态势,以期为相关研究人员或政策制定者提供参考。
2 数据来源与研究方法
2.1 数据来源
表1 CO2化工利用主要研究方向检索要素
| 主要技术分类 | 中文关键词 | 检索式 |
|---|---|---|
| CO2制主要化学品 | 二氧化碳、CO2、甲醇、甲酸、乙酸、二甲醚 | TS=("Carbon Dioxide*" or CarbonDioxide* or CO2) and (hydrogenation or "Carbon monoxide" or CO) and (methanol or "methyl alcohol" or "formic acid*" or "acetic acid" or DME or " Dimethyl ether") |
| CO2 热化学转化为甲烷 | 二氧化碳、CO2、热解、热化学、加氢、一氧化碳、甲烷 | 直接甲烷化:TS=("Carbon Dioxide*" or CarbonDioxide* or CO2) and (methane or CH4) and (pyrolysis* or thermo-chemical or thermochem* or hydrogenation or H2) |
| 间接甲烷化:TS=("Carbon Dioxide*" or CarbonDioxide* or CO2) AND ("Carbon monoxide" or CO) and (methane or CH4) and (pyrolysis* or thermo-chemical or thermochem* or hydrogenation or H2) | ||
| CO2 热化学转化为合成气 | 二氧化碳、CO2、热解、热化学、合成气、甲烷干法重整 | TS=("Carbon Dioxide" or CarbonDioxide or CO2) and ("synthesis gas*" or "synthetic gas*" or syngas) and (pyrolysis* or thermo-chemical or thermochem*) |
| TS=("Carbon Dioxide" or CarbonDioxide or CO2) and (methane or CH4) and ("synthesis gas*" or "synthetic gas*" or syngas) and ("dry reform*") | ||
| CO2制尿素 | 二氧化碳、CO2、氨、尿素 | TS=("Carbon Dioxide*" or CarbonDioxide* or CO2) and ammonia* and Urea |
| CO2制水杨酸 | 二氧化碳、CO2、水杨酸 | TS=("Carbon Dioxide" or CarbonDioxide or CO2) and ("Salicylic acid") |
| CO2制聚碳酸酯、聚氨酯、丙烯酸酯、聚碳酸亚乙酯等可降解材料/塑料 | 二氧化碳、CO2、聚碳酸酯、聚氨酯、丙烯酸酯、聚碳酸亚乙酯、可降解材料 | TS=("Carbon Dioxide*" or CarbonDioxide* or CO2) and (Polycarbonate*) and ("organic carbonate*" or "Ethylene carbonate*" or epoxypropane or "propylene epoxide" or "propylene oxide") |
| TS=("Carbon Dioxide*" or CarbonDioxide* or CO2) and (epoxypropane or "propylene epoxide*" or "propylene oxide" or "Non isocyanate*" or diisocyanate* or cyclonitride* or (epoxide* and isocyanate*)) and polyurethane* | ||
| TS=("Carbon Dioxide*" or CarbonDioxide* or CO2) and Acrylate* and TS=(Ethene or ethylene) | ||
| TS=("Carbon Dioxide*" or CarbonDioxide* or CO2) and ("Polycarbonate lemon ester" or PLC) | ||
| TS=("Carbon Dioxide*"or CarbonDioxide* or CO2) and ("biodegradable polymer*") | ||
| TS=("Carbon Dioxide*" or CarbonDioxide* or CO2) and ((epoxypropane or "propylene epoxide" or "propylene oxide") or ((epoxypropane or "propylene epoxide" or "propylene oxide") and ("ethylene oxide" or oxirane or oxacyclopropane)) or ((epoxypropane or "propylene epoxide" or "propylene oxide") and ("Cyclohexene oxide" or Epoxycyclohexane))) | ||
| CO2合成燃料 | 液体燃料、低烯烃、柴油、航空燃料 | TS=("Carbon Dioxide*" or CarbonDioxide* or CO2) and (hydrogenation or CH4 or methane or methanol or H2 or "Carbon monoxide" or CO) and ("liquid fuel*" or "liquid hydrocarbon" or synfuel* or "light olefin*" or "lower olefin*" or aromatic*or "liquid alkane*" or alkene* or gasoline or diesel or "jet fuel*") |
将上述检索式进行逻辑或(OR)组合检索,并进行去重、清洗,最终得到CO2化工利用领域论文20 539篇。本文的数据统计口径说明如下:论文统计时间窗为2001–2020年,文献类型为Article、Review,检索时间为2020年11月5日。
2.2 研究方法及工具
本文主要采用文献计量方法,对近20年来CO2化工转化利用领域的基础数据进行年代切块,设置每10年为一个时间块,从论文产出规模、学术影响力、国际合作、期刊及学科分布、研究主题等方面对比分析该领域两个10年的发展态势。本研究主要使用的计量与可视化分析工具有DDA、VOSviewer、Citespace和Excel等。
3 CO2化工产品利用领域发文态势分析
3.1 发文年代分布
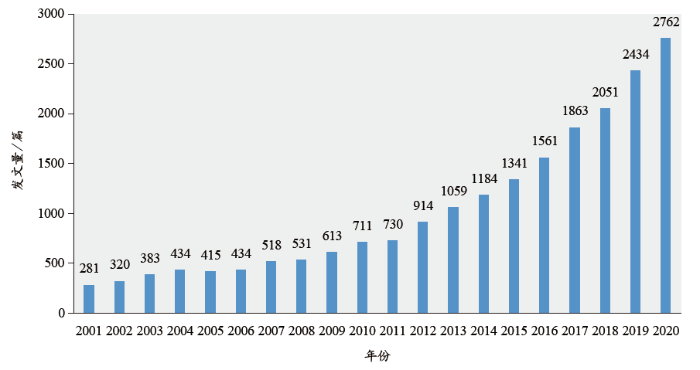
2001年至今,全球共发表CO2化工转化利用相关研究论文20 539篇。从图1可以看出,2001–2020年,该领域发文保持稳步增长态势;与2001–2010年相比,2011–2020年领域论文增速明显加快,全球研究规模显著扩大。
图1
3.2 发文国家/地区及国际合作分析
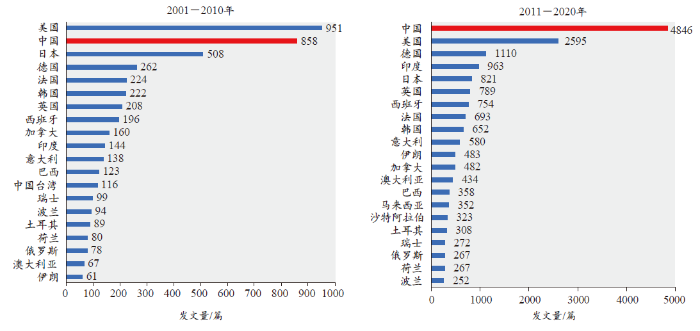
图2
图3
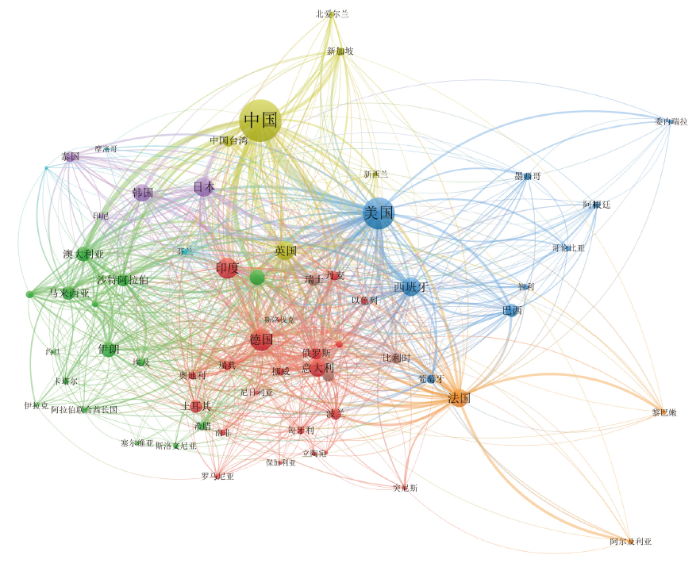
图4
图5
进一步用PageRank指标测度合作网络中节点的中心地位(见表2),可以发现中国在第二个时间窗中取代美国,成为合作网络中心。
表2 CO2化工转化利用领域国际合作网络PageRank值TOP20国家/地区
| 2001–2010年 | 2011–2020年 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 国家/地区 | PageRank值 | 排名 | 国家/地区 | PageRank值 | 排名 |
| 美国 | 0.134 | 1 | 中国 | 0.104 | 1 |
| 中国 | 0.079 | 2 | 美国 | 0.101 | 2 |
| 法国 | 0.073 | 3 | 英国 | 0.053 | 3 |
| 德国 | 0.060 | 4 | 德国 | 0.050 | 4 |
| 英国 | 0.050 | 5 | 法国 | 0.046 | 5 |
| 日本 | 0.040 | 6 | 西班牙 | 0.041 | 6 |
| 加拿大 | 0.038 | 7 | 意大利 | 0.033 | 7 |
| 西班牙 | 0.036 | 8 | 日本 | 0.030 | 8 |
| 意大利 | 0.033 | 9 | 澳大利亚 | 0.027 | 9 |
| 瑞士 | 0.028 | 10 | 加拿大 | 0.025 | 10 |
| 巴西 | 0.026 | 11 | 沙特阿拉伯 | 0.024 | 11 |
| 韩国 | 0.026 | 12 | 马来西亚 | 0.023 | 12 |
| 荷兰 | 0.023 | 13 | 印度 | 0.023 | 13 |
| 澳大利亚 | 0.022 | 14 | 韩国 | 0.021 | 14 |
| 比利时 | 0.016 | 15 | 荷兰 | 0.021 | 15 |
| 葡萄牙 | 0.015 | 16 | 瑞士 | 0.018 | 16 |
| 印度 | 0.015 | 17 | 比利时 | 0.016 | 17 |
| 波兰 | 0.014 | 18 | 伊朗 | 0.015 | 18 |
| 俄罗斯 | 0.014 | 19 | 巴西 | 0.014 | 19 |
| 阿根廷 | 0.014 | 20 | 丹麦 | 0.013 | 20 |
从国际合作区域分析来看,中国在该领域进行国际合作最多的国家为美国、英国、日本、澳大利亚、加拿大等,其中美国、英国、澳大利亚与中国合作论文数量的排名有所上升,日本、加拿大的排名有所下降;从2001–2010年、2011–2020年各国家/地区与中国的合作论文数量占其本国/地区国际合作论文总数的比例来看(表3),除日本外,中国与大多数国家/地区的合作伙伴关系越来越密切。
表3 CO2化工转化利用领域中国的TOP20合作国家/地区
| 2001–2010年 | 2011–2020年 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 国家/地区 | 与中国合作 论文数/篇 | 国际合作 论文总数/篇 | 占比/% | 国家/地区 | 与中国合作 论文数/篇 | 国际合作 论文总数/篇 | 占比/% |
| 日本 | 45 | 83 | 54.22 | 美国 | 522 | 1188 | 43.94 |
| 美国 | 31 | 230 | 13.48 | 英国 | 150 | 497 | 30.18 |
| 英国 | 13 | 78 | 16.67 | 澳大利亚 | 122 | 281 | 43.42 |
| 加拿大 | 13 | 68 | 19.12 | 日本 | 110 | 320 | 34.38 |
| 新加坡 | 12 | 20 | 60.00 | 加拿大 | 83 | 250 | 33.20 |
| 德国 | 8 | 100 | 8.00 | 德国 | 61 | 487 | 12.53 |
| 韩国 | 5 | 43 | 11.63 | 新加坡 | 57 | 85 | 67.06 |
| 澳大利亚 | 4 | 31 | 12.90 | 中国台湾 | 38 | 83 | 45.78 |
| 伊朗 | 4 | 13 | 30.77 | 沙特阿拉伯 | 37 | 209 | 17.70 |
| 瑞士 | 3 | 45 | 6.67 | 法国 | 35 | 442 | 7.92 |
| 法国 | 2 | 114 | 1.75 | 韩国 | 34 | 201 | 16.92 |
| 中国台湾 | 2 | 18 | 11.11 | 荷兰 | 30 | 183 | 16.39 |
| 比利时 | 2 | 17 | 11.76 | 巴基斯坦 | 27 | 91 | 29.67 |
| 瑞典 | 2 | 13 | 15.38 | 瑞典 | 20 | 101 | 19.80 |
| 中国香港 | 2 | 9 | 22.22 | 西班牙 | 19 | 394 | 4.82 |
| 意大利 | 2 | 50 | 4.00 | 泰国 | 17 | 100 | 17.00 |
| 芬兰 | 1 | 8 | 12.50 | 新西兰 | 16 | 29 | 55.17 |
| 荷兰 | 1 | 30 | 3.33 | 丹麦 | 16 | 103 | 15.53 |
| 沙特阿拉伯 | 1 | 5 | 20.00 | 意大利 | 16 | 285 | 5.61 |
| 巴林 | 1 | 1 | 100.00 | 中国香港 | 15 | 51 | 29.41 |
注:占比为各国家/地区与中国的合作论文数量占本国/地区国际合作论文总数的比例;中国数据未包含港澳台地区数据。
3.3 学术影响力分析
被引频次是测度论文学术影响力的基本指标。为使得不同年份、不同学科领域的被引频次规模可比,本研究采用国家/地区的被引频次世界份额(即国家/地区的被引频次除以同年份、同领域的世界被引频次)和消除研究规模影响的归一化指标CNCI进行学术影响力测度。2001–2010年,美国、中国和日本是该领域被引频次世界份额的TOP3国家,美国以较大的优势领先中国等其余国家/地区。2011–2020年,中国CO2化工转化利用领域的学术影响力超过美国,跃居第一位,但与美国的差距并不大(如图6)。
图6
从TOP10国家的CNCI值来看,2001–2010年,美国、西班牙、英国、德国和加拿大位居前列,均超过了TOP10国家CNCI均值;与前10年相比,后10年进步最大是法国和中国,其中法国从第6位上升至第3位,中国从第9位上升至第5位,且均超过了TOP10国家CNCI均值(如图7),但与美英等国仍存在一定差距。
图7
3.4 发文期刊分析
从表4可以看出,2001–2010年与2011–2020年CO2化工转化利用领域论文发文期刊变化较大。通过前后两个时间窗TOP10发文期刊的对比,发现前10年排在前4位的期刊Catalysis Today、Energy & Fuels、Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research在第二个10年的排名下降至后5位,而前10年排名在后3位的Fuel和Applied Catalysis B-Environmental在后10年跃升至前5位。此外,后10年新增ACS Catalysis、Journal of CO2 Utilization、Catalysis Science & Technology等刊冲入前10位。
表4 2001–2010年和2011–2020年CO2化工转化利用领域TOP20发文期刊
| 2001–2010年 | 2011–2020年 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 期刊名称 | 论文量/篇 | 2020IF | 期刊名称 | 论文量/篇 | 2020IF |
| Applied Catalysis A-General | 229 | 5.706 | International Journal of Hydrogen Energy | 683 | 5.816 |
| Catalysis Today | 156 | 6.766 | Fuel | 480 | 6.609 |
| Energy & Fuels | 139 | 3.605 | ACS Catalysis | 394 | 13.084 |
| Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research | 105 | 3.764 | Applied Catalysis B-Environmental | 315 | 19.503 |
| Catalysis Letters | 103 | 3.186 | Journal of CO2 Utilization | 312 | 7.132 |
| Journal of Catalysis | 103 | 7.920 | Energy & Fuels | 284 | 3.605 |
| International Journal of Hydrogen Energy | 97 | 5.816 | Catalysis Today | 280 | 6.766 |
| Fuel | 81 | 6.609 | Catalysis Science & Technology | 251 | 6.119 |
| Applied Catalysis B-Environmental | 76 | 19.503 | Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research | 242 | 3.764 |
| Journal of Molecular Catalysis A-Chemical | 73 | n/a | RSC Advances | 236 | 3.361 |
| Journal of Supercritical Fluids | 67 | 4.577 | Applied Energy | 229 | 9.746 |
| Journal of Physical Chemistry C | 66 | 4.126 | Energy | 228 | 7.147 |
| Chinese Journal of Catalysis | 64 | 8.271 | Energy Conversion and Management | 215 | 9.709 |
| Journal of the American Chemical Society | 54 | 15.419 | Chemcatchem | 209 | 5.686 |
| Fuel Processing Technology | 50 | 7.033 | Journal of Physical Chemistry C | 209 | 4.126 |
| Journal of Physical Chemistry B | 50 | 2.991 | Journal of the American Chemical Society | 201 | 15.419 |
| Journal of Power Sources | 49 | 9.127 | Applied Catalysis A-General | 201 | 5.706 |
| Journal of Physical Chemistry A | 47 | 2.781 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 185 | 13.273 |
| Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis | 47 | 5.541 | Catalysts | 180 | 4.146 |
| Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics | 45 | 3.676 | Green Chemistry | 180 | 10.182 |
3.5 学科交叉分析
2001–2010年、2011–2020年CO2化工转化利用领域论文所涉及的TOP10 WoS学科基本相同,相应的排名也接近,其中Chemistry, Physical、Engineering, Chemical、Energy & Fuels三个WoS学科是该领域论文的主要分布学科。总体而言,CO2化工转化利用领域的研究涉及化学、物理、环境、工程等学科的交叉融合,例如,研究CO2参与化工产品制备过程中的化学反应机理;探究CO2在环境保护方面的应用,如利用CO2制备可降解塑料。两个时间窗相比,该学科领域论文涉及Engineering和Environmental学科的论文比重和排名提升相对较多(表5)。
此外,本文通过赫尔芬达多样性指数(PDIV指数)来测度和反映某个学科领域的论文在其所涉及的WoS学科上分布的集中或者分散程度,从而反映该学科领域的学科交叉度。表5中给出了基于TOP10学科领域的学科交叉度。该领域论文的学科交叉度在2011–2020年相比2001–2010年略微有所提升。
表5 2001–2020年CO2化工转化利用领域TOP10 WoS学科多样性指数
| 2001–2010年 | 2011–2020年 | 2001–2020年 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 学科名称 | 论文 量/篇 | 学科名称 | 论文 量/篇 | 学科名称 | 论文 量/篇 |
| Chemistry, Physical | 1674 | Chemistry, Physical | 4939 | Chemistry, Physical | 6613 |
| Engineering, Chemical | 1364 | Engineering, Chemical | 4470 | Engineering, Chemical | 5834 |
| Energy & Fuels | 813 | Energy & Fuels | 4245 | Energy & Fuels | 5058 |
| Chemistry, Multidisciplinary | 513 | Chemistry, Multidisciplinary | 2893 | Chemistry, Multidisciplinary | 3406 |
| Environmental Sciences | 482 | Environmental Sciences | 1302 | Environmental Sciences | 1785 |
| Chemistry, Applied | 397 | Materials Science, Multidisciplinary | 1191 | Materials Science, Multidisciplinary | 1491 |
| Polymer Science | 314 | Green & Sustainable Science & Technology | 992 | Electrochemistry | 1236 |
| Materials Science, Multidisciplinary | 300 | Engineering, Environmental | 959 | Chemistry, Applied | 1208 |
| Electrochemistry | 280 | Electrochemistry | 956 | Engineering, Environmental | 1203 |
| Engineering, Environmental | 244 | Thermodynamics | 862 | Green & Sustainable Science & Technology | 1087 |
| 多样性指数 | 0.845 | 多样性指数 | 0.851 | 多样性指数 | 0.849 |
4 研究热点及发展趋势分析
4.1 热点研究主题分析
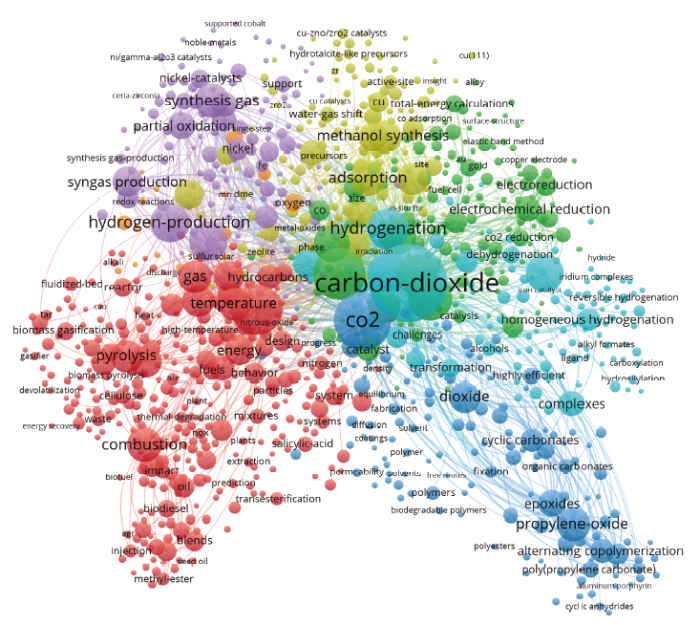
图8
图9
4.2 研究领域发展趋势分析
在分析CO2化工转化利用领域发展趋势时,本文利用CiteSpace突变词探测功能,对2011–2020年的基础数据进行年代切片,设置每一年为一个时间切片,对每个切片中突现关键词进行探测,最终得到表6。分析发现近十年该领域的研究制备产品热点从CO2制可降解塑料转移到CO2制低烯烃,制备工艺也从加氢热解转移至电化学反应。
表6 2011–2020年至今CO2化工产品利用领域突现词概况
| 序号 | 关键词 | 突现强度 | 开始年份 | 结束年份 | 2011–2020年 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | propylene oxide | 31.18 | 2011 | 2014 | ▃▃▃▃▂▂▂▂▂▂ |
| 2 | alternating copolymerization | 22.51 | 2011 | 2015 | ▃▃▃▃▃▂▂▂▂▂ |
| 3 | cyclohexene oxide | 18.47 | 2011 | 2014 | ▃▃▃▃▂▂▂▂▂▂ |
| 4 | poly(propylene carbonate) | 17.45 | 2011 | 2015 | ▃▃▃▃▃▂▂▂▂▂ |
| 5 | salen complexe | 14.66 | 2011 | 2014 | ▃▃▃▃▂▂▂▂▂▂ |
| 6 | CO | 12.9 | 2011 | 2012 | ▃▃▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂ |
| 7 | supercritical carbon dioxide | 12.45 | 2011 | 2017 | ▃▃▃▃▃▃▃▂▂▂ |
| 8 | mild condition | 11.86 | 2011 | 2016 | ▃▃▃▃▃▃▂▂▂▂ |
| 9 | coupling reaction | 11.78 | 2011 | 2016 | ▃▃▃▃▃▃▂▂▂▂ |
| 10 | diiminate zinc catalyst | 11.75 | 2011 | 2015 | ▃▃▃▃▃▂▂▂▂▂ |
| 11 | hydrogen | 11.4 | 2011 | 2012 | ▃▃▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂ |
| 12 | co2/epoxide copolymerization | 10.78 | 2011 | 2015 | ▃▃▃▃▃▂▂▂▂▂ |
| 13 | platinum | 10.49 | 2011 | 2012 | ▃▃▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂ |
| 14 | asymmetric alternating copolymerization | 10.21 | 2011 | 2016 | ▃▃▃▃▃▃▂▂▂▂ |
| 15 | hydrosilylation | 13.09 | 2012 | 2015 | ▂▃▃▃▃▂▂▂▂▂ |
| 16 | mechanistic aspect | 12.92 | 2013 | 2016 | ▂▂▃▃▃▃▂▂▂▂ |
| 17 | homogeneous hydrogenation | 12.9 | 2013 | 2014 | ▂▂▃▃▂▂▂▂▂▂ |
| 18 | defined iron catalyst | 9.54 | 2013 | 2015 | ▂▂▃▃▃▂▂▂▂▂ |
| 19 | organic carbonate | 10.49 | 2014 | 2016 | ▂▂▂▃▃▃▂▂▂▂ |
| 20 | electrochemical reduction | 9.84 | 2016 | 2018 | ▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▃▂▂ |
| 21 | si engine | 10.88 | 2017 | 2018 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▂▂ |
| 22 | lower olefin | 10.65 | 2018 | 2020 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▃ |
图10
图11
5 结语
2001–2020年CO2化工转化利用领域发文量保持稳步增长发展态势,与2001–2010年相比,2011–2020年论文增速明显加快,全球研究规模显著扩大。该领域发文期刊变化较大,对比前后两个时间窗的TOP10发文期刊,发现前10年排名在后3位的Fuel和Applied Catalysis B-Environmental在后10年跃升至前5位,后10年TOP中新增ACS Catalysis、Journal of CO2 Utilization、Catalysis Science & Technology等期刊。该领域论文学科交叉度2011–2020年较2001–2010年略有提升。相比2001–2010年的热点研究主题CO2合成甲烷并进一步制合成气以及CO2加环氧丙烷制聚碳酸酯,2011–2020年研究热点在制品产品和工艺上均有所增加,如增加了CO2加氢电解制甲醇/甲酸、CO2加碳酸盐制聚碳酸酯以及CO2制生物质燃料。
总体来看,2001–2020年中国CO2化工转化利用领域的发展态势有以下表现:在成果产出规模方面,较之2001–2010年,2011–2020年中国发文量增速较快,增长4.6倍,超过美国,跃居全球第1位;在学术影响力方面,绝对影响力略超美国,位居世界第1,相对影响力有较大提升,从第9位上升至第5位,但与美英等国仍存在一定差距。从国际合作来看,在国际合作网络中取代美国成为网络中心,合作国家也越来越多。近10年中国在该领域的研究热点由CO2制甲酸、合成气向制甲醇及低烯烃转移,美国的研究热点从CO2制备氨、甲醇、生物燃料转移至CO2制备合成气。
参考文献
Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis[R/OL]
(2021-08-06)[2021-11-22]. https://www.ipcc.ch/report/sixth-assessment-report-working-group-i/.
“碳达峰”与“碳中和”——绿色发展的必由之路[EB/OL]
(
IEA(2020), CCUS in Clean Energy Transitions[R/OL]
[2021-10-27]. Paris: IEA,
中国气候路径报告[R/OL]
(
Carbon Capture, Utilization & Storage[EB/OL]
(2021-01-27)[2021-11-24]. https://www.energy.gov/carbon-capture-utilization-storage.
Carbon dioxide utilization: A paradigm shift with CO2 economy
[J].
Industrial carbon dioxide capture and utilization: state of the art and future challenges
[J].
Challenges in the greener production of formates/formic acid, methanol, and DME by heterogeneously catalyzed CO2 hydrogenation processes
[J].The recent advances in the development of heterogeneous catalysts and processes for the direct hydrogenation of CO to formate/formic acid, methanol, and dimethyl ether are thoroughly reviewed, with special emphasis on thermodynamics and catalyst design considerations. After introducing the main motivation for the development of such processes, we first summarize the most important aspects of CO capture and green routes to produce H. Once the scene in terms of feedstocks is introduced, we carefully summarize the state of the art in the development of heterogeneous catalysts for these important hydrogenation reactions. Finally, in an attempt to give an order of magnitude regarding CO valorization, we critically assess economical aspects of the production of methanol and DME and outline future research and development directions.
Catalysis for the valorization of exhaust carbon: from CO2 to chemicals, materials, and fuels. technological use of CO2
[J].
Recent advances in enzymatic catalysis for preparation of high value-added chemicals from carbon dioxide
[J].
With the rapid development of modern industry, coal, petroleum, natural gas and other fossil fuels have been excessively consumed, along with an increasing large quantities of greenhouse gases (e.g. carbon dioxide, CO2) are produced. It is urgent to develop sustainable green energy and abate the detriment of carbon dioxide on global environment. CO2 is a cheap carbon source that can be converted into high value-added chemicals by chemical, photochemical, electrochemical or enzymatic methods to realize the recycling of CO2. It is a win-win strategy to solve the energy and environmental crisis caused by global carbon emissions. Inspired by natural CO2 metabolic process, enzymatic transformation provides an alternative strategy for efficient recycling of CO2. Compared with traditional chemical, photochemical or electrochemical methods, the enzymatic route holds advantages of green, high efficiency, mild and excellent selectivity, which is expected to bring new revolutionary opportunities for efficient utilization of CO2. Thus, in this present review, we firstly introduce the brief background about enzymatic conversion for CO2 capture, sequestration and utilization. Next, we depict six major routes of the CO2 metabolic process in cells, which are taken as the inspiration source for the construction of enzymatic systems in vitro. Subsequently, recent advances in enzymatic conversion of CO2 that catalyzed by various single enzymes and multi-enzyme cascade systems are systematically reviewed. Some emerging approaches for construction of immobilized single-or multi-enzyme systems, directed evolution and artificial modification of enzymes, and cofactor regulation during the enzymatic processes are also discussed. Finally, the defects and shortcomings of enzymatic approaches are summarized, and the future perspectives are finally put forward. Based on this present review, we aim to provide theoretical reference and practical basis for more efficient enzymatic utilization of CO2 to produce high value-added chemicals.
Utilization of carbon dioxide in polyurethane
[J].
碳捕获、利用与封存(CCUS)技术发展现状及应用展望[EB/OL]
.(2021-07-12)[2021-11-24]. www.craes.cn/xxgk/zhxw/202107/W020210715614159269764.pdf.