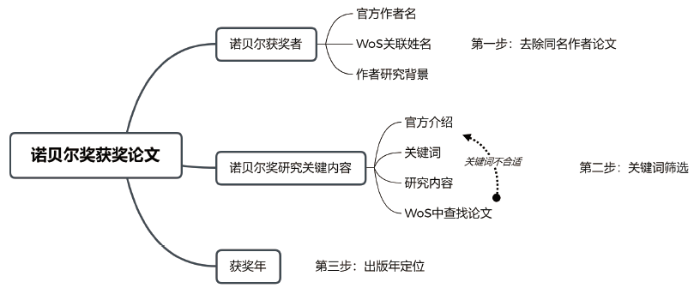
1 引言
2020年,教育部官网公布了对《关于完善高校学科评估制度,促进教育治理体系和能力现代化的提案》的答复,提案答复中明确表示坚持和完善代表作制度,要聚焦标志性学术成果,强调标志性学术成果的创新内容和学术贡献,关注代表性论文对标志性成果的支撑度和关联度[1]。
现今被广泛使用的评价方法主要是同行评议法和基于指标体系的定量评价。在我国明确提出代表作评价制度之后,对于定量评价有效性的讨论一度甚嚣尘上,我们要承认客观证据的必要性,也要承认一些良好指标对被评估对象的概括能力。科学计量学兴起于20世纪中叶,是一门对科学本身进行定量研究的学科,其核心问题是通过定量方法探寻科学活动的内在规律和特征[2]。很多已有研究表明,在大多数领域,论文或者科研人员获得的引用频次与同行之间的认可程度存在着正相关[3,4]。在科研评价应用场景中,科学计量学界针对引文指标的普遍共识是,在规范的标准化应用前提下,引文可以作为反映成果“学术影响力”的有效指标,但不能作为评价研究“质量”的直接或唯一指标。同时,专家的定性分析,既耗时又昂贵,一些主观因素的影响也难以排除,定性评价也有其不可避免的局限性[5]。评价学术论文聚焦标志性学术成果,需要采用“计量评价与专家评价相结合”的方式。
代表性成果强调创新内容和学术贡献,针对代表作的定量评价需要选取一批具有原始创新的论文为代表,深入分析其文献计量特征,为代表作制度的定量评价找到合适的评价指标。
在众多国际科学奖项中,诺贝尔科学奖作为最具权威的科学奖项得到了各界认可。诺贝尔科学奖所激励的是对人类社会发展有重大影响的原始性创新[6]。本文选取诺贝尔奖获奖论文,分析其文献计量特征,为代表作制度中代表作的筛选和定量评价提供参考。
2 数据来源与研究方法
2.1 数据来源
图1
数据采集时间为2020年6月17日。从WoS数据库和InCites数据库中获取相应指标数据。从共50位获奖者的论文中,筛选出73篇获奖论文。
2.2 研究方法
2.2.1 指标选择
选取诺奖论文的期刊分布、被引频次、学科规范化引文影响力(CNCI)、被引半衰期等指标进行统计分析[8],概括诺奖论文在经典指标上的表现。
2.2.2 TOPCM指标选取
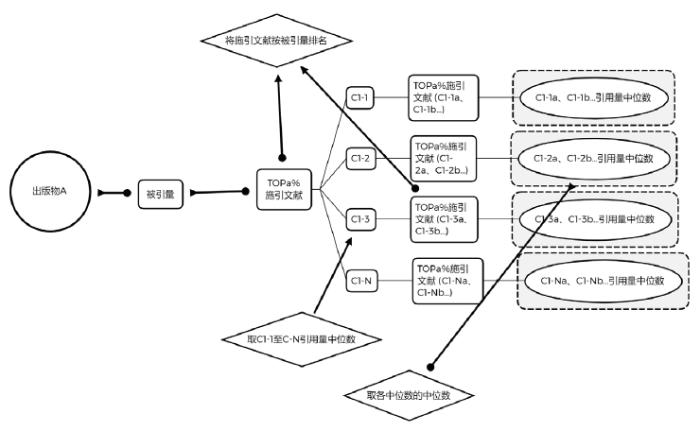
TOPCM指标是针对未达到期待引用但有影响力的出版物提出的算法[9]。代表性成果具备了原始创新,是后续研究的启发者,但可能存在自身被引频次未达期待的情况。为了更好地筛选与评价自身引用不足的代表性成果,引入TOPCM指标对诺奖论文进行分析,为代表性成果的指标选择提供参考。
TOPCM指标应用算法如下:
(1)首先选择一个出版物,设为A。
(2)将A的被引频次计为CIT(A),如果A的被引频次为ⅹ,我们取其被引频次的1%,例如ⅹ=248,则248×1%=2.48,取大于它的最小整数,即2.48取3。第一级引文为被引量排名前3的三篇文献分别为C1-1、C1-2、C1-3。取他们被引量的中位数为μ1。
TOPCM2(A) = μ1
(3)对第一级得到的所有文献分别重复步骤2,得到二级引文(C1-1a、C1-1b…、C1-2a、C1-2b…)。分别对各第二级引文取中位数,然后取所有第二级引文的中位数μ2。
$\operatorname{TOPCM} 3(\mathrm{~A})=\frac{2}{3}\left(\mu 1+\frac{1}{2} \mu 2\right)=\frac{2}{3} \mu 1+\frac{1}{3} \mu 2$
类似地,我们可以定义第n+1代引文影响力的TOPCM-N的值。
$\operatorname{TOPCM}(n+1)(\mathrm{A})=\sum_{i=1}^{n} \frac{1}{\mathrm{i} !} \mu \mathrm{i} / \sum_{i=1}^{n} \frac{1}{\mathrm{i} !}$
具体计算流程如图2所示。
图 2
3 研究结果
3.1 文献计量特征分析
3.1.1 诺奖论文总被引频次普遍较高
对2000–2019年的所有诺奖论文的被引频次进行统计。被引频次从出版后开始计算,截至2020年6月16日。
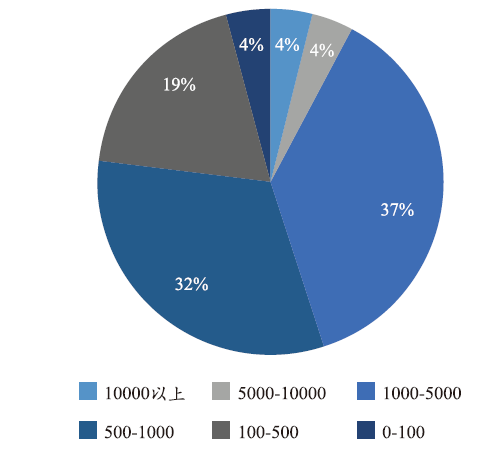
诺奖论文的被引频次分布显示在图3中。被引用的范围分布很广,从21次到14 996次,分布最多的区间是1 000~5 000次,四分之三的论文引用次数达到500次以上。3篇诺奖论文的引用达1万次以上,且有3篇论文的引用低于100次。进一步分析这3篇被引频次低于100的文章,一篇为2010年诺奖获得者Edwards在2001年发表的关于体外受精的社论(editorial),而他做出关键突破的文章集中发表在20世纪70年代,这篇社论是之后的总结,可能因此未获得更多的引用。另外两篇引用低于100的文章是2003年诺奖获得者关于核磁共振的论文,获奖者在利用磁共振可视化不同结构方面取得了开创性的发现,这些发现促成了现代磁共振成像MRI的发展,这代表了医学诊断和研究领域的突破。但文章发表时磁共振在医学应用层面还处于未完善阶段,这可能是文章未取得较多引用的原因。而对于被引频次在100到300之间的论文,作为高影响力的论文并没有获得足够高的引用,我们在后文引入新的指标进行详细分析。总体来说,诺奖论文普遍具有较高的被引频次。
图3
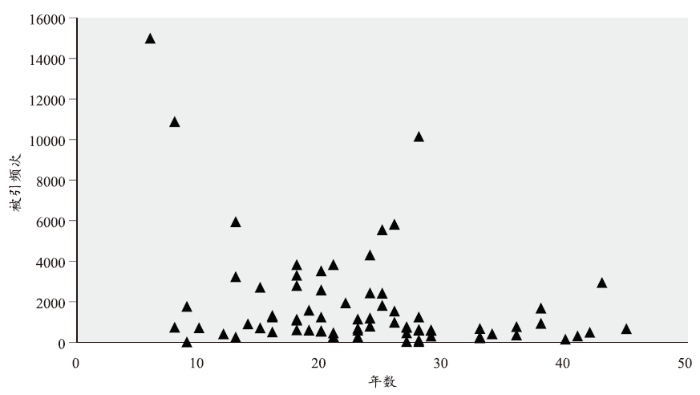
我们把诺奖论文从出版到获奖的时间间隔定义为诺奖论文的测试期。如图4所示,诺贝尔奖的测试期大致在10到30年之间。在小于10年的测试期间内,有2人的获奖论文被引用超过1万次,可见,有少数被引频次极高的获奖者在很短的时间内获得了诺贝尔奖。例如,山中伸弥(Shinya Yamanaka)仅仅花了6年的时间。被引频次与诺贝尔奖的测试期之间存在反比趋势。
图4
3.1.2 大多数诺奖论文被引半衰期长
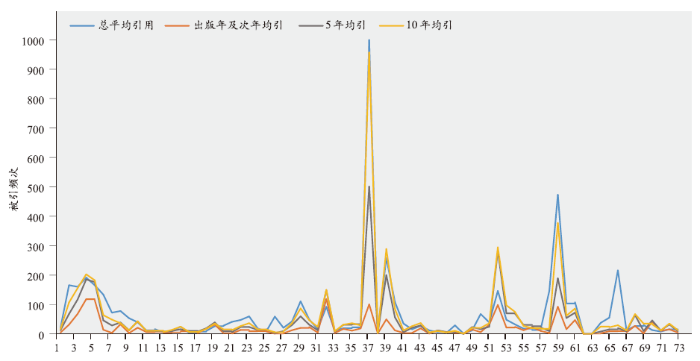
比较73篇诺奖论文截至2020年6月的总平均引用,发表年及次年、发表后5年、发表后10年的平均引用4个指标,结果如图5所示,发表后10年的平均引用更接近总平均引用。大部分论文的被引频次在5~10年间会达到稳定状态,有研究表明诺奖论文的总体平均引用更接近5年的平均引用水平[10]。本文的研究针对近20年诺贝尔生理学或医学奖的获奖论文,结果显示,10年的平均引用更接近总平均引用。诺奖的评选考虑对领域的突出贡献,具有重大创新,在一定意义上是新颖、超前的,获得科学界的普遍认可,而在应用层面的发展需要较长时间。已有文献表明,大部分诺奖论文的引用呈规律分布[11],从图中也可以看出诺奖论文不同年份的引用在趋势上的一致性。
图5
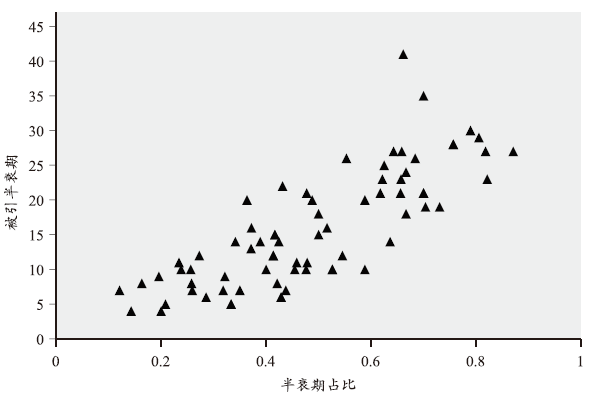
被引半衰期(Cited Half-life)反映的是文献自身老化的速度,被引半衰期越长,文献的影响越深远。以期刊为例,一般研究型期刊的被引半衰期相对长,时效性期刊的被引半衰期相对短。统计诺奖论文的被引半衰期,并计算诺奖论文被引半衰期占出版至今总年数的比例。结果如图6所示,大部分诺奖论文的被引半衰期较长,55篇论文的被引半衰期达10年以上,26篇达20年以上。同时考虑到诺奖论文出版时间较早,计算了被引半衰期占总年数的比例,28篇占50%以上,60篇占30%以上。
图6
3.1.3 诺奖论文大多发表在高影响力期刊上
图7
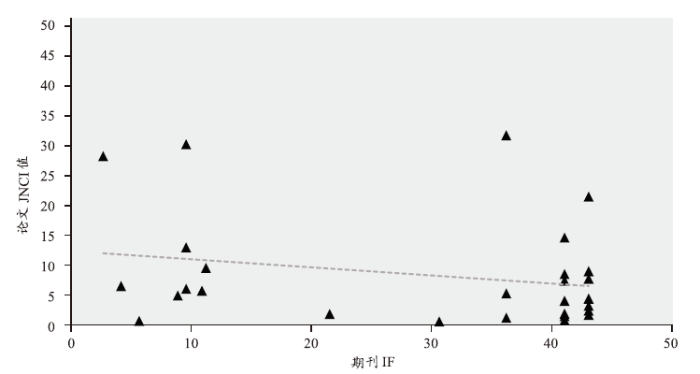
期刊规范化的引文影响力(JNCI)是对文献发表在特定期刊上的被引频次进行规范化,即每篇论文的JNCI值为该论文实际被引频次与该期刊上发表的同出版年、同文献类型论文的平均被引频次的比值。它揭示出那些超过平均水平并提高了期刊被引频次的研究工作。论文所属期刊是论文的重要特征,在考虑期刊影响因子的同时考虑JNCI值,可以更全面地衡量论文的影响力,剔除期刊自身的光环。但是比较JNCI值要考虑所属学科。例如,一个科研工作者的CNCI指标高于平均值,JNCI指标低于平均值,这可能意味着该科研工作者在其论文所研究的领域获得了比平均水平更多的引用,但是这位科研工作者论文发表的期刊具有非常高的被引频次(例如Science或Nature),因此该论文被引频次低于这本期刊上论文的平均被引频次。比较能够查到JNCI值的28篇获奖论文,如图8所示,只有两篇论文的JNCI值小于1,大部分论文的JNCI值达到了2以上。诺奖论文不仅发表在高影响因子的期刊上,其JNCI值也非常高。
图8
3.1.4 诺奖论文CNCI值普遍非常高
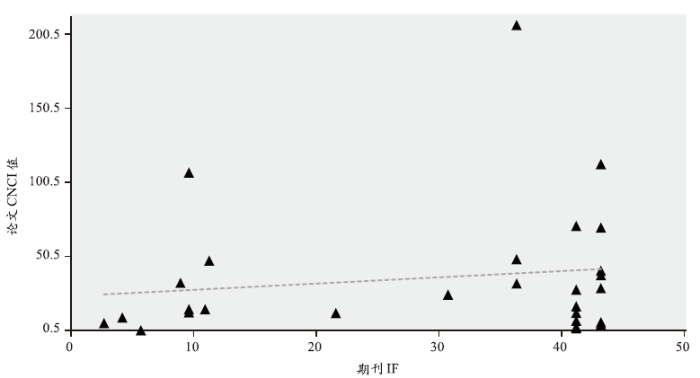
学科规范化的引文影响力(CNCI)是对不同文献类型、不同出版年、不同学科领域进行归一化后的评价指标,是一个十分有价值且无偏的引文影响力指标。一篇文献的CNCI是通过其实际被引次数除以同文献类型、同出版年、同学科领域文献的期望被引次数获得的。如果CNCI的值为1,说明该组论文的被引表现与全球平均水平相当;CNCI值大于1,表明该组论文的被引表现高于全球平均水平;小于1,则低于全球平均水平。CNCI值排除了学科、文章类型以及出版年的差异,可以作为衡量文章质量的一个重要指标。我们统计了能够查到CNCI值的28篇获奖论文,除一篇文章小于1外,其他文章的CNCI值都大于2,且有20篇大于10。诺奖文章的CNCI值普遍非常高,且与期刊IF呈正相关(图9)。
图9
3.1.5 诺奖论文施引文献CNCI值普遍较高
针对少数高质量论文被引频次不高的情况,我们考虑施引文献质量来弥补被引指标的不足。我们统计了28篇诺奖论文的CNCI 值和其施引文献的CNCI值及篇均被引频次,结果如表1所示。除第28篇社论外,其余27篇诺奖论文的施引文献CNCI值普遍较高, 平均达到2.04。按照被引频次大小将28篇诺奖论文分为两组,发现不同被引频次之间的诺奖论文其施引文献CNCI值和篇均被引次数均没有显著差异。
表1 诺奖论文施引文献指标
| 被引频次分组 | 序号 | 诺奖论文 | 施引文献 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 获奖年 | 出版年 | CNCI值 | CNCI值 | 篇均被引频次 | ||
| 第1组 | 1 | 2012 | 2006 | 210.50 | 1.32 | 40.50 |
| 2 | 2006 | 1998 | 114.42 | 1.42 | 60.20 | |
| 3 | 2011 | 1998 | 107.77 | 2.02 | 93.60 | |
| 4 | 2019 | 1995 | 49.97 | 1.90 | 81.93 | |
| 5 | 2019 | 2001 | 72.08 | 1.75 | 77.73 | |
| 6 | 2019 | 1999 | 71.08 | 2.01 | 95.25 | |
| 7 | 2019 | 2001 | 41.62 | 1.81 | 81.37 | |
| 8 | 2018 | 2000 | 49.95 | 2.97 | 68.53 | |
| 9 | 2018 | 1996 | 39.98 | 3.28 | 76.89 | |
| 10 | 2011 | 1996 | 32.89 | 2.33 | 119.58 | |
| 11 | 2013 | 1993 | 27.45 | 1.34 | 75.56 | |
| 12 | 2018 | 1999 | 29.85 | 3.26 | 93.24 | |
| 13 | 2014 | 2005 | 33.47 | 1.71 | 43.21 | |
| 14 | 2018 | 1992 | 17.91 | 2.93 | 80.34 | |
| 第2组 | 15 | 2018 | 2003 | 12.49 | 2.55 | 80.93 |
| 16 | 2016 | 2000 | 15.33 | 2.19 | 88.70 | |
| 17 | 2016 | 1993 | 25.53 | 2.53 | 118.96 | |
| 18 | 2016 | 1998 | 12.65 | 2.49 | 114.00 | |
| 19 | 2016 | 1992 | 9.53 | 2.01 | 103.37 | |
| 20 | 2014 | 2006 | 15.07 | 1.89 | 48.74 | |
| 21 | 2014 | 2004 | 12.95 | 1.73 | 58.19 | |
| 22 | 2017 | 1998 | 7.17 | 1.44 | 84.70 | |
| 23 | 2013 | 1993 | 6.01 | 1.60 | 97.04 | |
| 24 | 2018 | 1997 | 5.60 | 2.10 | 78.59 | |
| 25 | 2017 | 1994 | 3.04 | 1.40 | 86.72 | |
| 26 | 2018 | 2005 | 4.73 | 2.82 | 81.89 | |
| 27 | 2017 | 1992 | 2.03 | 1.78 | 94.99 | |
| 28 | 2010 | 2001 | 0.70 | 0.59 | 10.58 | |
3.1.6 特定诺奖论文的TOPCM指标值较高
表2 TOPCM值
| 作者 | 出版物 | 出版时间 | 被引量 | μ1 | μ2 | TOPCM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| James P. Allison | Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America | 1997 | 291 | 783 | 728.5 | 764.8 |
| Tasuku Honjo | International Immunology | 2005 | 268 | 866 | 533 | 755 |
| Michael W. Young | Science | 1994 | 276 | 619 | 952 | 730 |
图10
图11
图12
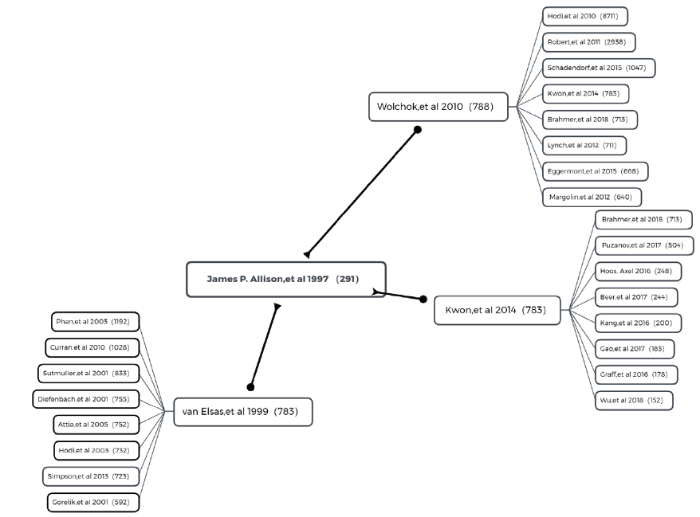
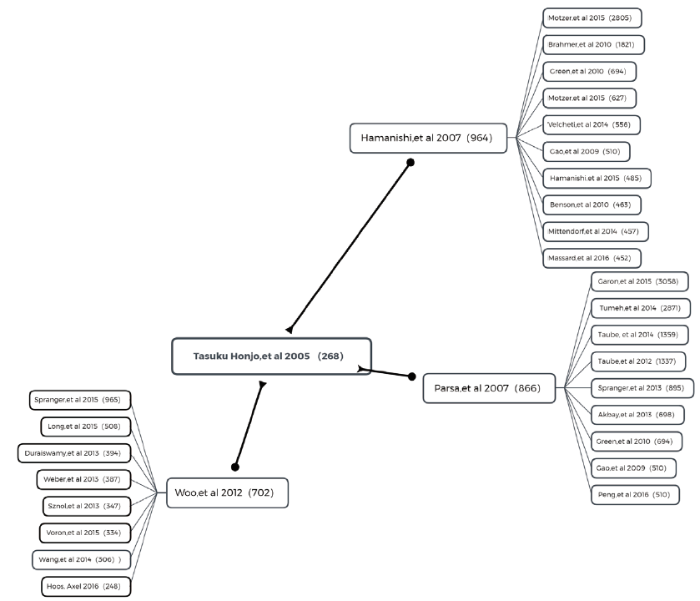
100多年来,科学家一直试图使免疫系统参与抗癌工作。2018年由于发现抑制负向免疫调节的新型癌症疗法,James P. Allison和Tasuku Honjo共同获得了诺贝尔医学奖或生理学奖。James P. Allison在20世纪90年代,利用小鼠实验证实阻击CTLA-4会解除T细胞受到的束缚,使其全力对抗癌细胞[12]。Tasuku Honjo在研究了PD-L1可以通过与PD-1的相互作用来抑制免疫反应的机制之后,在2005年进一步研究了PD-1缺陷小鼠中免疫原性差的B16黑色素瘤细胞向肝脏的血源性扩散受到抑制[13]。而这两篇论文作为他们获得诺奖的重要研究,均未获得很高的引用。我们对其引文进行分析,结果如图10和图11所示。对于James P. Allison在1997年发表论文的三篇一代引文(图10),两篇是基于CTLA-4 的单克隆抗体“伊匹单抗”的临床试验,还有一篇是CTLA-4相关机制的进一步研究 [14,15,16]。进一步分析第二代引文,引用前两篇的大部分是相关改进的临床试验,值得注意的是,引用Wolchok论文的有一篇被引频次达到了8 000以上,是关于伊匹单抗提高转移性黑色素瘤患者生存率的论文[17]。同理,我们分析Tasuku Honjo在2005年发表的论文(图11),三篇一代引文是关于免疫抑制机制的[18,19,20],而第二代引文中大部分是相关抗体的临床试验和进一步研究。
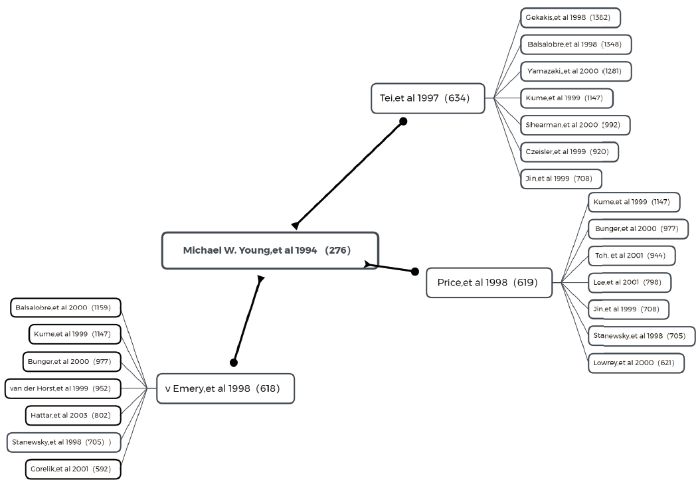
2017年获得诺贝尔奖的Michael W. Young在1994年发表的论文[21]被引频次为267,而其发表于1998年、引用了该论文的文章[22],一同被认定为获奖论文,获得了634次引用。我们对论文内容进行具体分析,1994年,Michael Young发现了第二个时钟基因“timeless”,该基因能够编码正常昼夜节律所需要的关键蛋白——TIM蛋白,研究者发现,当TIM同PER绑定后,两种蛋白就会进入到细胞核中,在细胞核中阻断period基因的活性关闭抑制反馈回路。这样的调节性反馈机制能够解释细胞中蛋白水平发生波动的机制,但仍然存在无法解释的问题,即到底是什么控制着波动(摆动)的频率。1998年,Michael Young鉴别出了另外一个关键基因doubletime,其能够编码名为DBT的蛋白,该蛋白能够减缓PER蛋白的积累,这能够帮助阐明这种昼夜节律波动是如何被调节来精密适应每天24小时循环的。也就是说1998年的论文引用了1994年的论文,在其研究基础上进一步解释了昼夜节律波动的原理。
4 讨论
我们分析了诺奖论文的文献计量特征,从期刊、施引文献、定量评价三个角度为我们目前的代表作评估提供建议。
4.1 重视学科内权威期刊的积极表征作用
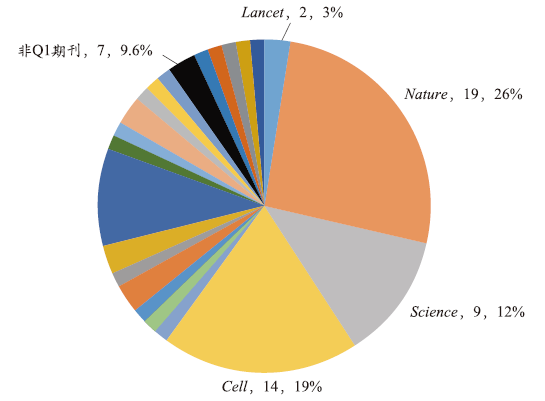
期刊影响因子本身包含了同行评审的认可信息及其对论文投稿与稿件遴选的积极导向功能,期刊影响因子的学术质量表征意义是毋庸置疑的[23]。研究发现大多数诺奖论文发表在影响因子大于30的期刊上,其中Science,Cell,Nature三大顶尖期刊发表的论文数占总量的一半以上。诺贝尔奖获得者更倾向将研究结果发表在学科顶尖期刊中,而不是泛泛的SCI期刊[24]。具稀缺性的核心期刊由于有充分的经费保障、实力雄厚的学术编辑队伍以及更好的制度激励,它们的审稿流程和用稿标准往往更为严格,甚至近乎苛刻,这就在相当程度上有效避免了对论文的“误判”,进而保证所刊论文的相对优质性[25]。《关于破除科技评价中“唯论文”不良导向的若干措施(试行)》的通知也明确指出,鼓励发表三类高质量论文,即具有国际影响力的国内科技期刊、业界公认的国际顶级或重要科技期刊的论文[26]。因此,在进行代表作遴选时,建议重视国际顶尖期刊和学科内权威期刊,合理利用学科内权威期刊的积极表征作用。
期刊影响因子可在一定程度上表征其学术质量的优劣,但影响因子与学术质量间并非成正比关系,比如不能说影响因子为5.0的期刊一定优于影响因子为4.0的期刊,影响因子不具有这种对学术质量进行精确定量评价的功能,同时不同学科之间没有可比性。教育部、科技部联合发布的《关于规范高等学校SCI论文相关指标使用树立正确评价导向的若干意见》里也明确提出“坚决摒弃以刊评文,评价重点是论文的创新水平和科学价值,不把SCI论文相关指标作为直接判断依据”[27]。因此,在进行代表作遴选时,对于普通期刊不简单以期刊影响因子作为定量比较的依据。
4.2 引入施引文献指标辅助筛选代表作
已有相关研究指出,单篇论文影响力评价指标必须兼顾反映施引文献的质量。为了兼顾评价施引文献影响力,陆续引入了施引文献h指数、TVF等指标[28]。代表作的评价中也应当关注施引文献影响力。
TOPCM指标是针对未达到期待引用但有影响力的出版物提出的算法,与利用谷歌PageRank算法来识别“宝石”论文有着类似之处[29],高被引论文的引用比普通论文的引用更有价值。诺奖论文作为具备原始创新的重要成果,被认为具有重大突破和前沿性发现,少数诺奖论文本身被引频次不高,却被高被引论文引用。最初的研究包含了基本的想法,但它的后续文章确实发展了它,因此吸引了更多的引文。本文统计了符合条件的诺奖论文的TOPCM值,并具体分析了该部分诺奖论文及其引文的研究内容,TOPCM指标可以从符合条件的低被引论文中识别出强影响力论文,具有应用潜力,可用于代表作的筛选评价。但TOPCM指标的使用有一定限制,对被引周期和论文本身的被引频次有一定要求,其值只取决于几代引文中被引量最高的几篇。对于被引频次不足的论文,我们建议选取施引文献的CNCI值作为有效指标,来评价施引文献影响力,施引文献CNCI值能够规范出版年的差异,简洁有效。而施引文献CNCI是对施引文献整体的引文影响力进行评价,能够忽略出版年的差异,简单易获取。对于不符合TOPCM使用条件的论文,可以引入施引文献CNCI值作为施引文献的评价指标辅助筛选代表作。
4.3 因地制宜,定量评价与定性评价结合
目前国际上的科研评估整体呈现出定性与定量相结合的多元发展趋势,相比于人文学科,自然学科会更多的参考引文指标。因此,考虑到成本与同行评审的主观性,代表作的遴选也需要定量指标的辅助。“量化”标准本身有其价值和统计意义上的合理性,关键在于如何使用量化信息。诺贝尔奖论文无疑是学术界公认的高品质论文,我们以诺奖成果为代表,分析其计量学特征,从已经得到广泛认可的经典指标中进一步筛选,找到最适合代表作遴选的关键指标,为代表作的筛选提供可行参考。
我们的研究发现,诺奖论文普遍具有较高的引用次数。同时,被引频次与测试期成反比,这种现象在被引频次极高时更加明显。科睿唯安的“引文桂冠奖”便是基于世界范围内高被引论文的文献计量分析,目前已成功预测多名诺奖得主,而诺贝尔奖的获得无疑是世界顶尖同行做出的评审结果。虽然论文品质高低不取决于被引量甚或论文长短, 但被引量体现着学术影响力[30]。尤金·加菲尔德博士发现引文分析能够成为同行评议的一种补充,用于确保评价的客观性或者为专家提供更多的信息。人们不应该用论文和引文数据来代替阅读以及来评估科研人员的成果,进而代替同行的判断。应该利用一系列标准化指标进行综合分析。当我们通过被引频次位于前百分之一、前千分之一乃至前万分之一的论文来定量分析一位科研人员时,可以充分表明该科研人员贡献了一些非常有价值、甚至有重要意义的东西,当他发表了多项这类成果的时候,我们可以更准确地判断该科研人员的研究具有重要的学术影响力[31]。因此,被引频次依旧是重要指标。
引用指标的使用需要考虑被引周期。被引半衰期较长一般代表着出版的文章比较经典,才历久不衰,诺奖文章的引用规律也体现了这一点。对于出版时间较长的文章,可以重点关注引用半衰期用于遴选代表性成果。
诺奖论文CNCI值普遍较高,在排除了学科和出版年影响的情况下,28篇诺奖论文中有20篇的CNCI值达到了20以上,结果并非巧合,这说明了CNCI值确实能够很好地反映学科领域内论文的影响力。
代表作的推行应当采取定量评价与专家评价相结合的方式,很多同行评审专家也会将文献计量指标作为重要参考[32]。选取最具代表性的计量指标,充分发挥定量指标直观、客观的优势,构建定量与定性相结合的评价体系。本文从引用角度出发,总结梳理遴选代表作的重要指标,考虑权威期刊的表征作用,关注施引文献质量弥补被引指标的局限。但以上指标是以论文的被引量为基础,指标之间有同源性,由于论文被引指标有其局限性,后续可以引入社交媒体评价等指标来丰富定量评价体系,这是未来的研究方向。
参考文献
《关于完善高校学科评估制度,促进教育治理体系和能力现代化的提案》的答复
[EB/OL]. (
Peer reviews and bibliometric indicators: a comparative study at a Norwegian university
[J].
Correlations between bibliometrics and peer evaluation for all disciplines: the evaluation of Brazilian scientists
[J].
'Peer review' for scientific manuscripts: Emerging issues, potential threats, and possible remedies
[J].Reviewers play a vital role in ensuring quality control of scientific manuscripts published in any journal. The traditional double blind peer review, although a time-tested method, has come under increasing criticism in the face of emerging trends in the review process with the primary concern being the delays in completion of the review process. Other issues are the inability to detect errors/fraud, lack of transparency, lack of reliability, potential for bias, potential for unethical practices, lack of objectivity, inconsistencies amongst reviewers, lack of recognition and motivation of reviewers. Alternative options to classical peer review being propagated are: open review, immediate self-publication using preprint servers, nonselective review focusing primarily on the scientific content, and post-publication review. These alternative review processes, however, may suffer from the inability to validate quality control. In addition, anecdotal instances of peer review frauds are being reported more often than earlier. Suggested means to ensure quality of peer review process includes:(a) each journal to have its own database of reviewers, (b) verification of email IDs of reviewers provided by authors along with details of their institutions, (c) ensure credibility of reviewers before requesting for review, (d) check for plagiarism at the editorial level, (e) editors to distinguish between a good review from a possible biased/bad review, and (f) give recognition for reviewers once in a year. To conclude, quickness of review and publication should not dictate the scientific publication process at the cost of quality of contents.
Understanding Noble Prizes winning articles: A bibliometric analysis
[J].
InCites—基于Web of Science 权威数据的科研评估工具
[DB/OL]. (
Scientific influence is not always visible: The phenomenon of under-cited influential publications
[J].
Bibliometric analysis of Nobelists' awards and landmark papers in physiology or medicine during 1983-2012
[J].
Manipulation of T cell costimulatory and inhibitory signals for immunotherapy of prostate cancer
[J].
PD-1 blockade inhibits hematogenous spread of poorly immunogenic tumor cells by enhanced recruitment of effector T cells
[J].Since metastasis is the major cause of death for cancer patients, there is an urgent need to develop new therapies to control hematogenous dissemination of cancer cells. Previously we and others demonstrated a novel mechanism that allows tumors to escape from the host immune response by expressing PD-L1 which can negatively regulate immune response through the interaction with PD-1, an immunoinhibitory receptor belonging to the CD28 family. In this study, we report that hematogenous spread of poorly immunogenic B16 melanoma cells to the liver was inhibited in PD-1-deficient mice. After inoculation to spleen, PD-L1 was induced on tumor cells, which did not express PD-L1 in vitro. As compared with wild-type mice, intrasplenic injection of B16 cells into PD-1-deficient mice showed enhanced induction of effector T cells in spleen, prolonged T cell proliferation and cytokine production, and augmented homing of effector T cells to tumor sites in the liver, resulting in accumulation of effector T cells in the tumor sites. PD-1 blockade by genetic manipulation or antibody treatment inhibited not only hematogenous dissemination of B16 melanoma cells to the liver on the C57BL/6 background, but also dissemination of CT26 colon cancer cells to the lung on the BALB/c background. These results suggest that PD-1 blockade may be a powerful tool for treatment of hematogenous spread of various tumor cells.
Ipilimumab monotherapy in patients with pretreated advanced melanoma: a randomised, double-blind, multicentre, phase 2, dose-ranging study
[J].Ipilimumab is a human monoclonal antibody that blocks cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4 and has shown promising activity in advanced melanoma. We aimed to ascertain the antitumour efficacy of ipilimumab in patients with advanced melanoma.We undertook a randomised, double-blind, phase 2 trial in 66 centres from 12 countries. 217 patients with previously treated stage III (unresectable) or stage IV melanoma were randomly assigned a fixed dose of ipilimumab of either 10 mg/kg (n=73), 3 mg/kg (n=72), or 0.3 mg/kg (n=72) every 3 weeks for four cycles (induction) followed by maintenance therapy every 3 months. Randomisation was done with a permuted block procedure, stratified on the basis of type of previous treatment. The primary endpoint was best overall response rate (the proportion of patients with a complete or partial response, according to modified WHO criteria). Efficacy analyses were done by intention to treat, whereas safety analyses included patients who received at least one dose of ipilimumab. This study is registered with ClinicalTrials.gov, number NCT00289640.The best overall response rate was 11.1% (95% CI 4.9-20.7) for 10 mg/kg, 4.2% (0.9-11.7) for 3 mg/kg, and 0% (0.0-4.9) for 0.3 mg/kg (p=0.0015; trend test). Immune-related adverse events of any grade arose in 50 of 71, 46 of 71, and 19 of 72 patients at doses of 10 mg/kg, 3 mg/kg, and 0.3 mg/kg, respectively; the most common grade 3-4 adverse events were gastrointestinal immune-related events (11 in the 10 mg/kg group, two in the 3 mg/kg group, none in the 0.3 mg/kg group) and diarrhoea (ten in the 10 mg/kg group, one in the 3 mg/kg group, none in the 0.3 mg/kg group).Ipilimumab elicited a dose-dependent effect on efficacy and safety measures in pretreated patients with advanced melanoma, lending support to further studies at a dose of 10 mg/kg.Bristol-Myers Squibb.Copyright 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Ipilimumab versus placebo after radiotherapy in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer that had progressed after docetaxel chemotherapy (CA184-043): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial
[J].
Combination immunotherapy of B16 melanoma using anti-cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 (CTLA-4) and granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF)-producing vaccines induces rejection of subcutaneous and metastatic tumors accompanied by autoimmune depigmentation
[J].
Improved survival with ipilimumab in patients with metastatic melanoma
[J].
Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 and tumor-infiltrating CD8(+) T lymphocytes are prognostic factors of human ovarian cancer
[J].The ligands for programmed cell death 1 (PD-1), an immunoinhibitory receptor belonging to CD28/cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 4 family, are PD-1 ligand 1 and 2 (PD-Ls). Recent reports suggest that the aberrant expression of PD-Ls on tumor cells impairs antitumor immunity, resulting in the immune evasion of the tumor cells. Although an inverse correlation between the expression level of PD-Ls and patients' prognosis has been reported for several malignant tumors, the follow-up period was limited because of the lack of the antibody (Ab) applicable to paraffin-embedded specimens. Here we generated a new Ab against PD-1 ligand 1 (PD-L1) and analyzed the expression level of PD-Ls in human ovarian cancer using paraffin-embedded specimens. Patients with higher expression of PD-L1 had a significantly poorer prognosis than patients with lower expression. Although patients with higher expression of PD-1 ligand 2 also had a poorer prognosis, the difference was not statistically significant. A significant inverse correlation was observed between PD-L1 expression and the intraepithelial CD8(+) T lymphocyte count, suggesting that PD-L1 on tumor cells directly suppresses antitumor CD8(+) T cells. Multivariate analysis showed the expression of PD-L1 on tumor cells and intraepithelial CD8(+) T lymphocyte count are independent prognostic factors. The PD-1/PD-L pathway can be a good target for restoring antitumor immunity in ovarian cancer.
Loss of tumor suppressor PTEN function increases B7-H1 expression and immunoresistance in glioma
[J].
Immune inhibitory molecules LAG-3 and PD-1 synergistically regulate T-cell function to promote tumoral immune escape
[J].
Block in nuclear-localization of period protein by a 2nd clock mutation timeless
[J].In wild-type Drosophila, the period protein (PER) is found in nuclei of the eyes and brain, and PER immunoreactivity oscillates with a circadian rhythm. The studies described here indicate that the nuclear localization of PER is blocked by timeless (tim), a second chromosome mutation that, like per null mutations, abolishes circadian rhythms. PER fusion proteins without a conserved domain (PAS) and some flanking sequences are nuclear in tim mutants. This suggests that a segment of PER inhibits nuclear localization in tim mutants. The tim gene may have a role in establishing rhythms of PER abundance and nuclear localization in wild-type flies.
Double-time is a novel Drosophila clock gene that regulates PERIOD protein accumulation
[J].We have isolated three alleles of a novel Drosophila clock gene, double-time (dbt). Short- (dbtS) and long-period (dbtL) mutants alter both behavioral rhythmicity and molecular oscillations from previously identified clock genes, period and timeless. A third allele, dbtP, causes pupal lethality and eliminates circadian cycling of per and tim gene products in larvae. In dbtP mutants, PER proteins constitutively accumulate, remain hypophosphorylated, and no longer depend on TIM proteins for their accumulation. We propose that the normal function of DOUBLETIME protein is to reduce the stability and thus the level of accumulation of monomeric PER proteins. This would promote a delay between per/tim transcription and PER/TIM complex function, which is essential for molecular rhythmicity.
国际重大创新性论文的发表倾向分析——以1989-2019年诺贝尔生理学或医学奖获得者论文为例
[J].
《关于破除科技评价中“唯论文”不良导向的若干措施(试行)》的通知
[EB/OL]. (
《关于规范高等学校SCI论文相关指标使用树立正确评价导向的若干意见》的通知
[EB/OL]. (
Finding scientific gems with Google’s PageRank algorithm
[J].
How do NIHR peer review panels use bibliometric information to support their decisions?
[J].Bibliometrics is widely used as an evaluation tool to assist prospective R&D decision-making. In the UK, for example, the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) has employed bibliometric analysis alongside wider information in several awarding panels for major funding schemes. In this paper, we examine various aspects of the use of bibliometric information by members of these award selection panels, based on interviews with ten panel members from three NIHR panels, alongside analysis of the information provided to those panels. The aim of the work is to determine what influence bibliometrics has on their decision-making, to see which types of bibliometric measures they find more and less useful, and to identify the challenges they have when using these data. We find that panel members broadly support the use of bibliometrics in panel decision-making, and that the data are primarily used in the initial individual assessment of candidates, playing a smaller role in the selection panel meeting. Panel members felt that the most useful measures of performance are normalised citation scores and the number or proportion of papers in the most highly cited % (e.g. 5, 10%) for the field. Panel members expressed concerns around the comparability of bibliometrics between fields, but the discussion suggested this largely represents a lack of understanding of bibliometric techniques, confirming that effective background information is important. Based on the evidence around panel behaviour and concerns, we set out guidance around providing bibliometrics to research funding panels.