1 引言
集成光学的概念是1969年由美国贝尔实验室的S. E. Miller博士提出的[1]。集成光学是研究媒质薄膜中的光学现象以及光学元器件集成化的一门学科。它要解决的实质问题是获得具有不同功能、不同集成度的集成光路,以实现光学信息处理系统的集成化和微小化[2,3]。集成光学是采用集成方法研究光学器件和混合光学-电子学器件系统的一门学科。集成光学建立在光电子学、光波导理论、激光技术和微电子学的微细加工工艺发展的基础之上,是光子学的一个重要分支[4]。集成光学的任务是将传统的光学元器件和系统微型化,并按照新的物理观点将这些元器件或系统“集成”,以形成具有多种功能的集成光学体系。集成光学是当今光子学领域的发展前沿之一,它主要研究集成在一个平面衬底上的光学器件和光电子学领域的理论、技术与应用,是光学发展的必由之路和高级阶段[5,6,7]。集成光学以光波导、激光器、光调制器、接收器等光子和电子元件为核心集成起来,并以具有一定功能的体系为标志;光纤、各种集成光学器件已被广泛应用于光通信系统中;非通信领域——传感技术方面的应用也有了很大的发展。类似于电子计算机中有大量的集成电路一样,集成光路将成为光计算机中的主要部分[5,7-10]。
本文基于Web of Science核心合集中Science Citation Index Expanded (SCI-Expanded)数据库,对2007–2016年期间发表的集成光学领域文献进行了分析,从而揭示集成光学领域的宏观发展趋势。
2 数据来源
2.1 数据来源
本文利用Web of Science核心合集中SCI-Expanded数据库的数据作为数据源,采用的检索式为:TS=“integrat* optics”,时间跨度为:2007–2016,检索时间为:2017-06-17,文献类型包括文章(Article)、评论(Review)、会议摘要(Meeting Abstract)、快报(Letter)等全部文献类型。将数据源导入Incites平台,从影响力和期刊分区的角度,对部分机构和国家的情况进行了分析。利用Thomson Data Analyzer (TDA)软件对原始数据进行了清洗,其中对作者关键词进行了完整的清理和整理,比如将index和refractive index合并为refractive index,将on-chip和chip合并为chip,optical wave-guides和 wave-guides合并为wave-guides,将和modulator意义一致的detector合并为modulator,将silicon photonics和silicon合并为主题词silicon。经过合并和删除,使分析数据更加准确。最后,利用TDA对作者关键词进行了分析。
2.2 数据库介绍
InCitesTM:是基于科睿唯安Web of ScienceTM核心合集七大索引数据库的数据进行出版物计数和指标计算。七大索引数据库合集涵盖了1.2万种期刊、16万种会议录以及5.3万本学术典籍。目前InCitesTM提供了1980 年至今的全部文献类型的出版物。数据与基线每两个月更新一次。
基本科学指标数据库(Essential Science Indicators,ESI):是基于科睿唯安Web of Science (SCIE/SSCI)所收录的全球1.1万多种学术期刊的1 000多万条文献记录而建立的计量分析数据库。该数据库着重从文献引用角度反映学术影响力,可作为衡量科学研究绩效、跟踪科学发展趋势的基本分析评价工具。
2.3 指标解释
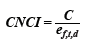
其中
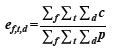
公式中的 e 为基线值或期望被引率,c 为被引频次,p 为论文数量,f 为学科领域,t 为出版年,d 为文献类型。
ESI高被引论文:是指近10年内发表的SCI论文且被引次数排在相应学科领域全球前1%以内。高被引论文能够在一定程度上反映某领域最热门的研究方向。该目录每两个月更新一次。
Q1区期刊论文占比:在科睿唯安的JCR报告中,按照期刊影响因子数值大小排序,处于所在领域前25%的期刊称为Q1区期刊。对于一个国家或者机构,其发表在Q1区期刊论文数量占其发表的所有SCI论文数量的百分比,可以从一个角度说明其论文的影响力情况。
本文从论文数量、CNCI以及Q1区期刊论文百分比等多个方面来综合对比国家和机构的情况。
3 集成光学的发展态势
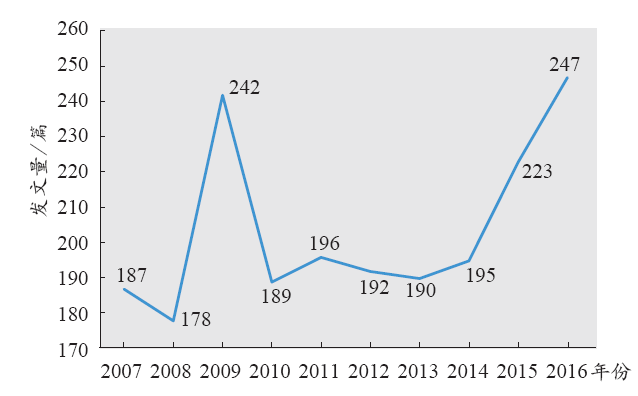
3.1 发文量年度情况
图1
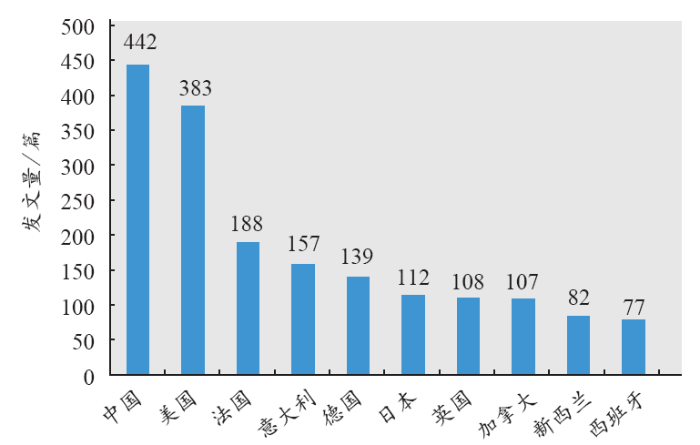
3.2 论文数量的国家分布
2007–2016年集成光学领域发文数量排名前10位的国家中(见图2),中国位列第1,发文442篇;排在第2位的是美国,发文383篇;其次是法国(188篇)、意大利(157篇)、德国(139篇)、日本(113篇)、英国(108篇)和加拿大(107篇)。
图2
从表1可以看出,发文量前10的国家中只有中国和日本的学科规范化引文影响力低于全球平均水平,英国最高,是全球平均水平的1.53倍,其次是美国(1.48);对于发表在Q1期刊的论文百分比(%),中国最低,美国最高。中国虽然在论文数量上具有优势,但是就论文的引文影响力而言却存在不足。美国的论文无论是数量还是引文影响力都表现不俗。英国虽然在数量上没有优势,但其影响力表现抢眼。
表1 集成光学领域发文量排名前10国家的论文数量、CNCI值及Q1期刊论文占比
| 国家 | 论文数/篇 | CNCI | 发表在Q1期刊的论文百分比/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 中国 | 442 | 0.65 | 36.96 |
| 美国 | 383 | 1.48 | 76.86 |
| 法国 | 188 | 1.01 | 58.79 |
| 意大利 | 157 | 1.16 | 63.16 |
| 德国 | 139 | 1.37 | 62.77 |
| 日本 | 112 | 0.65 | 65.14 |
| 英国 | 108 | 1.53 | 67.29 |
| 加拿大 | 107 | 1.31 | 76.64 |
| 新西兰 | 82 | 1.41 | 69.51 |
| 西班牙 | 77 | 1.08 | 69.74 |
3.3 集成光学领域主要研究机构
2007–2016年期间SCI收录的集成光学领域论文来自全球880个机构。其中发文量30篇以上的有机构14个,详见表2。发文数量位居第1位的是法国国家科学研究中心(CNRS,111篇);排在第2位的是美国加利福尼亚大学(University of California System,65篇);排在第3位的是中国科学院(55篇);接下来依次是中国的浙江大学(42篇)、法国的格勒诺布尔大学(Universite Grenoble Alpes,38篇)、荷兰的屯特大学(University of Twente,37篇)以及英国的南安普敦大学(University of Southampton,37篇)。
表2 发文量≥30篇的机构
| 机构名称 | WoS论文数/篇 | CNCI | 发表在Q1期刊的 论文百分比/% | 发表在Q1期刊的论文数量/篇 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 法国国家科学研究中心 | 111 | 0.98 | 58.49 | 62 |
| 加利福尼亚大学 | 65 | 1.54 | 76.92 | 50 |
| 中国科学院 | 55 | 0.53 | 23.64 | 13 |
| 浙江大学 | 42 | 0.79 | 53.66 | 22 |
| 格勒诺布尔大学 | 38 | 1.1 | 74.29 | 26 |
| 屯特大学 | 37 | 1.56 | 72.97 | 27 |
| 南安普敦大学 | 37 | 1.86 | 75.68 | 28 |
| 华中科技大学 | 36 | 0.7 | 27.78 | 10 |
| 巴黎-萨克雷大学 | 36 | 1.26 | 52.78 | 19 |
| 法国微电子研发机构 | 36 | 1.77 | 66.67 | 24 |
| 香港城市大学 | 34 | 0.34 | 73.53 | 25 |
| 意大利国家研究委员会 | 33 | 1.04 | 45.16 | 14 |
| 根特大学 | 31 | 1.87 | 80.65 | 25 |
| 米兰理工大学 | 31 | 1.37 | 80.00 | 24 |
学科规范化的引文影响力大于1的机构有加利福尼亚大学、格勒诺布尔大学、屯特大学、南安普顿大学、巴黎-萨克雷大学、法国微电子研发机构、意大利国家研究委员会(CNR)、根特大学以及米兰理工大学,这些机构的水平超出了世界平均水平;其中南安普敦大学和根特大学的表现尤为抢眼,影响力分别为全球平均水平的1.86倍和1.87倍;法国国家科学研究中心是0.98,接近全球平均水平;中国科学院、浙江大学、华中科技大学以及香港城市大学的影响力均低于全球平均水平。从发表在Q1期刊的论文百分比来看,根特大学比例最高,其次是加利福尼亚大学、南安普敦大学、格勒诺布尔大学、香港城市大学以及屯特大学;华中科技大学和中国科学院的Q1期刊论文百分比偏低。
表2的数据显示:加利福尼亚大学在论文数量和论文质量两方面都表现优异;根特大学和南安普敦大学则属于发文少而精;而国内相关科研机构不仅要提高论文数量,更要注重论文质量的提升。
3.4 热点关键词分析
作者关键词来自论文的题名、摘要和正文,对论文的中心内容有实质意义,作者关键词体现了文献研究内容,出现次数较多的关键词可以在一定程度上代表某个时间段内研究比较集中的内容,是研究中的瓶颈问题或者研究人员关注的热门话题。
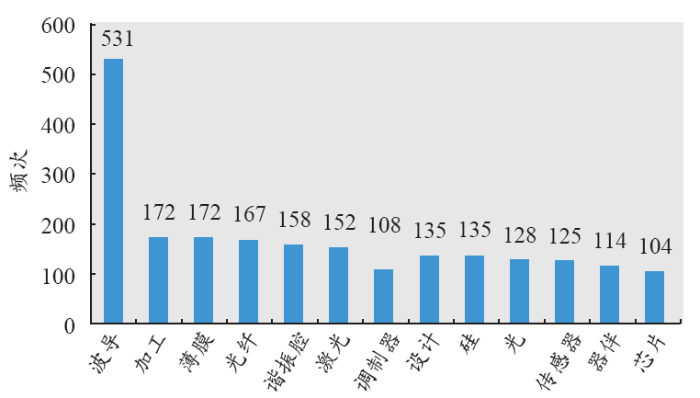
本文利用TDA对研究领域内的作者关键词进行了整理,详见图3。2007–2016年期间,出现次数较多的关键词为waveguides(波导)、fabrication(加工)、film(薄膜)、fiber(光纤)、resonators(谐振腔)、laser(激光)、modulator(调制器)、design(设计)、silicon(硅)、light(光)、sensors(传感器)、devices(器件)和chip(芯片)。其中波导出现的次数最多,高达531次,是排在第2位的加工(172次)的3.09倍。出现超过150次的关键词还有薄膜、光纤、谐振腔和激光器。
图3
波导是集成光学的研究热点,因为波导是一个基础器件,利用波导可以在实验上制备出谐振腔和调制器,同时波导也是硅光子的一个重要基础器件,基于此可以制备其他各类无源和有源的硅基光子器件;加工是排在第2位的关键词,因为设计完成以后就可以按照设计结果进行器件的加工制备,加工也有对波导和谐振腔等集成光学器件的加工;薄膜也是近10年集成光学研究的热点,因为制备波导、谐振腔和调制器等原件都需要先进行薄膜的制备;光纤的出现频次为167次,在光子集成中主要用于将光信号由光纤耦合进光子集成器件(包括波导,谐振腔等);谐振腔也是集成光学里的一个常见器件;激光出现频次也超过了150次。
3.5 高被引论文
2007–2016年期间,集成光学方向共有19篇论文入选2017年3/4月高被引论文(详见表3)。对19篇高被引论文的作者机构进行分析,发现涉及美国机构的最多,共有8篇;其次是英格兰和德国,各有3篇;西班牙有2篇;意大利、加拿大、葡萄牙、俄罗斯、苏格兰、新加坡、澳大利亚、比利时、芬兰、法国和中国各1篇。由于第一作者是论文的主要贡献者,所以对高被引论文第一作者的所属机构进行了统计。结果发现,高被引论文第一作者分别来自8个国家,依次为美国(7篇),德国和英国(各3篇),西班牙(2篇)及澳大利亚、法国、比利时和芬兰(各1篇)。
表3 高被引论文目录
| 标题 | 作者 | 来源出版物名称 | 出版年 | 被引频次 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chalcogenide photonics | Eggleton, Benjamin J.; Luther-Davies, Barry; Richardson, Kathleen | Nature Photonics | 2011 | 597 |
| Silica-on-silicon waveguide quantum circuits | Politi, Alberto; Cryan, Martin J.; Rarity, John G.; Yu, Siyuan; O'Brien, Jeremy L. | Science | 2008 | 492 |
| Heat assisted magnetic recording | Kryder, Mark H.; Gage, Edward C.; Mcdaniel, Terry W.; Challener, William A.; Rottmayer, Robert E.; Ju, Ganping; Hsia, Yiao-Tee; Erden, M. Fatih | Proceedings of the IEEE | 2008 | 477 |
| Progress on lanthanide-based organic-inorganic hybrid phosphors | Carlos, Luis D.; Ferreira, Rute A. S.; Bermudez, Veronica de Zea; Julian-Lopez, Beatriz; Escribano, Purificacion | Chemical Society Reviews | 2011 | 318 |
| Computer systems based on silicon photonic interconnects | Krishnamoorthy, Ashok V.; Ho, Ron; Zheng, Xuezhe; Schwetman, Herb; Lexau, Jon; Koka, Pranay; Li, GuoLiang; Shubin, Ivan; Cunningham, John E. | Proceedings of the IEEE | 2009 | 280 |
| Time-reversed lasing and interferometric control of absorption | Wan, Wenjie; Chong, Yidong; Ge, Li; Noh, Heeso; Stone, A. Douglas; Cao, Hui | Science | 2011 | 254 |
| Ultra-thin plasmonic optical vortex plate based on phase discontinuities | Genevet, Patrice; Yu, Nanfang; Aieta, Francesco; Lin, Jiao; Kats, Mikhail A.; Blanchard, Romain; Scully, Marlan O.; Gaburro, Zeno; Capasso, Federico | Applied Physics Letters | 2012 | 205 |
| Modes of subwavelength plasmonic slot waveguides | Veronis, Georgios; Fan, Shanhui | Journal of Lightwave Technology | 2007 | 175 |
| 标题 | 作者 | 来源出版物名称 | 出版年 | 被引频次 |
| Compact and highly efficient grating couplers between optical fiber and nanophotonic waveguides | Van Laere, Frederik; Roelkens, Guenther; Ayre, Melanie; Schrauwen, Jonathan; Taillaert, Dirk; Van Thourhout, Dries; Krauss, Thomas E.; Baets, Roe | Journal of Lightwave Technology | 2007 | 159 |
| Integrated optical devices for lab-on-a-chip biosensing applications | Estevez, M-Carmen; Alvarez, Mar; Lechuga, Laura M. | Laser & Photonics Reviews | 2012 | 144 |
| Nonreciprocal plasmonics enables giant enhancement of thin-film Faraday rotation | Chin, Jessie Yao; Steinle, Tobias; Wehlus, Thomas; Dregely, Daniel; Weiss, Thomas; Belotelov, Vladimir I.; Stritzker, Bernd; Giessen, Harald | Nature Communications | 2013 | 126 |
| Optically pumped planar waveguide lasers, Part I: Fundamentals and fabrication techniques | Grivas, Christos | Progress in Quantum Electronics | 2011 | 106 |
| Ion-exchanged glass waveguide technology: a review | Tervonen, Ari; West, Brian R.; Honkanen, Seppo | Optical Engineering | 2011 | 95 |
| A novel integrated quantum circuit for high-order W-state generation and its highly precise characterization | Heilmann, Rene; Graefe, Markus; Nolte, Stefan; Szameit, Alexander | Science Bulletin | 2015 | 60 |
| On-chip zero-index metamaterials | Li, Yang; Kita, Shota; Munoz, Philip; Reshef, Orad; Vulis, Daryl I.; Yin, Mei; Loncar, Marko; Mazur, Eric | Nature Photonics | 2015 | 57 |
| Integrated Photonic Electromagnetic Field Sensor Based on Broadband Bowtie Antenna Coupled Silicon Organic Hybrid Modulator | Zhang, Xingyu; Hosseini, Amir; Subbaraman, Harish; Wang, Shiyi; Zhan, Qiwen; Luo, Jingdong; Jen, Alex K. -Y.; Chen, Ray T. | Journal of Lightwave Technology | 2014 | 57 |
| Crystalline Waveguide Lasers in the Visible and Near-Infrared Spectral Range | Calmano, Thomas; Mueller, Sebastian | IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics | 2015 | 31 |
| Optically pumped planar waveguide lasers: Part II: Gain media, laser systems, and applications | Grivas, Christos | Progress in Quantum Electronics | 2016 | 19 |
| Single Carrier 168-Gb/s Line-Rate PAM Direct Detection Transmission Using High-Speed Selector Power DAC for Optical Interconnects | Mardoyan, Haik; Mestre, Miquel Angel; Rios-Mueller, Rafael; Konczykowska, Agnieszka; Renaudier, Jeremie; Jorge, Filipe; Duval, Bernadette; Dupuy, Jean-Yves; Ghazisaeidi, Amirhossein; Jenneve, Philippe; Achouche, Mohand; Bigo, Sebastien | Journal of Lightwave Technology | 2016 | 11 |
19篇高被引论文涉及37个机构,部分机构分布详见表4。哈佛大学和南安普敦大学各有两篇论文入选高被引论文,其他机构均只有一篇。
表4 高被引论文部分机构
| 机构 名称 | 哈佛 大学 | 南安普敦大学 | 斯图加特大学 | 悉尼 大学 | 得克萨斯大学 | 特伦特大学 | 华盛顿大学 | 劳瑞尔大学 | 耶鲁 大学 | 阿尔托大学 | 澳大利亚国立大学 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 论文 数/篇 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
4 结论
从发文数量上看:在国家层面,中国的研究成果最多,其次是美国;在机构层面,法国国家科学研究院的成果最多。从发文期刊上看:国家层面,美国在Q1区期刊上发表的论文的比例最高;机构层面,根特大学和米兰理工大学发表在Q1区期刊的成果所占比例最高。从影响力上看:国家层面,英国的学科规范化引文影响力最高,是全球平均水平的1.53倍,其次是美国,是全球平均水平的1.48倍,中国和日本的学科规范化引文影响力低于全球平均水平;机构层面,根特大学的学科规范化引文影响力最高,是全球平均水平的1.87倍,其次是南安普敦大学,是全球平均水平的1.86倍,中国研究机构的学科规范化引文影响力均低于世界平均水平。从高被引论文的分布来看,美国的高被引论文数量最多。
参考文献
Integrated optics - An introduction
[J].
Integrated-optics and new wave phenomena in optical-waveguides
[J].Research in integrated optics has two goals: One is to apply thin-film technology to the formation of optical devices and circuits. The other is the integration of a large number of optical devices on a small substrate, so forming an optical circuit reminiscent of the integrated circuit in microelectronics. The result is a new breed of optical devices in the form of miniature optical waveguides. They include lasers, modulators, switches, detectors, prisms, lenses, and polarizers, and many of them have efficiencies better than their bulk counterparts. Simple integrated optical circuits have also been constructed, and rapidly advancing semiconductor technology indicates that monolithic integrated optical circuits can readily be developed using GaAs-related compounds. In this paper, we review the state-of-the-art of integrated optics and explore new wave phenomena in optical circuits. The specific topics to be discussed are: light-wave couplers and m-line spectroscopy, refraction and reflection of light in thin films, normal modes of the uniform, the graded and the metal-clad waveguides, optics in tapered films, theory of corrugated waveguides, and more importantly, physics of various thin-film optical devices and the method of the circuit formation.
Introduction to integrated-optics
[J].
Electro-optic properties of indium/erbium-codoped lithium niobate crystal for integrated optics
[J].
Integrated optics on Lithium Niobate for sensing applications
[C].
Direct laser-writing of ferroelectric single-crystal waveguide architectures in glass for 3D integrated optics
[J].Direct three-dimensional laser writing of amorphous waveguides inside glass has been studied intensely as an attractive route for fabricating photonic integrated circuits. However, achieving essential nonlinear-optic functionality in such devices will also require the ability to create high-quality single-crystal waveguides. Femtosecond laser irradiation is capable of crystallizing glass in 3D, but producing optical-quality single-crystal structures suitable for waveguiding poses unique challenges that are unprecedented in the field of crystal growth. In this work, we use a high angular-resolution electron diffraction method to obtain the first conclusive confirmation that uniform single crystals can be grown inside glass by femtosecond laser writing under optimized conditions. We confirm waveguiding capability and present the first quantitative measurement of power transmission through a laser-written crystal-in-glass waveguide, yielding loss of 2.64鈥塪B/cm at 1530鈥塶m. We demonstrate uniformity of the crystal cross-section down the length of the waveguide and quantify its birefringence. Finally, as a proof-of-concept for patterning more complex device geometries, we demonstrate the use of dynamic phase modulation to grow symmetric crystal junctions with single-pass writing.
Integrated optics: Nanostructured silicon success
[J].
Towards a new crown indicator: Some theoretical considerations
[J].The crown indicator is a well-known bibliometric indicator of research performance developed by our institute. The indicator aims to normalize citation counts for differences among fields. We critically examine the theoretical basis of the normalization mechanism applied in the crown indicator. We also make a comparison with an alternative normalization mechanism. The alternative mechanism turns out to have more satisfactory properties than the mechanism applied in the crown indicator. In particular, the alternative mechanism has a so-called consistency property. The mechanism applied in the crown indicator lacks this important property. As a consequence of our findings, we are currently moving towards a new crown indicator, which relies on the alternative normalization mechanism.
Towards a new crown indicator: An empirical analysis
[J].AbstractWe present an empirical comparison between two normalization mechanisms for citation-based indicators of research performance. These mechanisms aim to normalize citation counts for the field and the year in which a publication was published. One mechanism is applied in the current so-called crown indicator of our institute. The other mechanism is applied in the new crown indicator that our institute is currently exploring. We find that at high aggregation levels, such as at the level of large research institutions or at the level of countries, the differences between the two mechanisms are very small. At lower aggregation levels, such as at the level of research groups or at the level of journals, the differences between the two mechanisms are somewhat larger. We pay special attention to the way in which recent publications are handled. These publications typically have very low citation counts and should therefore be handled with special care.
Shor’s Quantum Factoring Algorithm on a Photonic Chip
[J].