随着社会经济和科学技术的高速发展,对时间频率传递和同步的需求越来越高,特别是在基础科学、深空探测、现代高科技装备和系统中,时间的精确性及稳定性至关重要。基于光纤的时间频率传递成为未来高精度地面时间同步网络的主要发展趋势。该研究以INSPEC数据库为数据源,采用专业数据分析工具Thomson Data Analyzer(TDA)对光纤时间频率传递研究论文进行数据挖掘和定量分析,探讨该领域的研究现状、主要研究力量、研究热点及发展趋势,以期为时间频率科研工作者、决策者以及我国时间频率系统的发展、创新提供参考。
近年来,随着社会经济和科学技术的高速发展,特别是现代高精度原子钟的飞速发展,频率稳定度在10-16/s量级的频率振荡器及频率不确定度在10-18量级的光钟相继出现,现有的时间频率传输和同步技术已无法满足此类高精度原子钟时间频率比对的需求,亟需发展具有更高精度的时间频率传输与同步方法[1,2,3]。超高精度时间频率同步的重要性不仅体现在导航领域,在基础科学、深空探测、大地测量、国防安全、现代通信、金融和自动控制等领域也有着广泛而重要的应用。如在信息时代的现代化战争中,只有保证高精密、高准确的时间频率系统,才能实现体系内各兵种以及高精度武器设备的协同作战,否则就会影响通信、导航、雷达和电子对抗等高技术电子设备的有效性[4]。此外,在电离层特性研究、时频测控、校准及高精度的时间戳等很多科学研究领域,高精度时间传递都发挥着极其重要的作用。
发展独立自主的时间频率系统是我国建设独立强国的政治抉择,有无时间频率系统及其性能高低,体现了一个国家的科技综合实力、一种大国地位的竞争、一种战略制高点的争夺[5]。基于光纤链路的时频同步技术以其具有的低损耗、高稳定度优势而逐渐发展成为一种新型同步技术,世界各国均已开展此项技术的研究[6,7,8,9]。特别是天基时间同步网络的精度限制以及天基时同网络存在着体系复杂、实现周期长和安全方面的隐患,使得用光纤来进行时间信号的传递和检测成为高精度时间同步的主要方案之一[10,11]。
从文献计量角度探讨科学研究布局和发展态势是一种有效的途径和方法。为明确光纤时间频率传递研究在世界范围的研究布局和发展态势,本文基于Web of Knowledge平台的INSPEC数据库对该领域有关的文献进行计量学统计,探讨该领域的研究现状、研究重点及发展趋势,以期为时间频率科研工作者、决策者以及我国时间频率系统的发展、研究布局的规划等提供科学参考。
本工作选择Web of Knowledge平台的INSPEC数据库作为文献样本数据来源,利用光纤时间频率传递研究主题词构建检索策略,将检索结果进行人工判读并严格筛选,最终获得1976–2015年间(Inspect数据库最早索引至1969年)世界各国在光纤时间频率传递方面公开发表的论文共计1 320条(文献类型为journal paper和conference paper,检索时间为2016年1月18日)。以这些文献作为分析的数据集,借助美国汤森路透公司(科睿唯安)开发的Thomson Data Analyzer(TDA)分析工具进行文献数据挖掘,并结合Excel、Origin等工具进行统计和分析。
图1给出全球光纤时间频率传递研究论文数量的变化趋势,可以看出,论文整体上呈稳态增长趋势。国际上自1970年代末就开展了利用光纤进行时间频率传递的研究,到1980年代末论文数量一直处于较少状态;从1990年代初起,光纤时间频率传递研究呈现逐步发展态势,全球范围内其受关注程度日益增加。特别是进入21世纪后,随着离子光频标、飞秒激光器、频率合成器、激光控制器、光频测量技术的快速发展[2],掀起了利用光纤进行时间频率传递研究的热潮。论文数量虽处于波动状态但总体增速较快,2013年达到峰值(137篇)。中国虽在此研究领域起步较晚,但近几年的发展尤为迅速。
按照发文总量统计,图2给出全球范围内从事光纤时间频率传递研究的前10个主要国家的发文总量及其近3年发文量占其发文总量的百分比情况。可以看出,目前在该技术领域走在世界前列的主要有美国、日本和欧洲等国家或地区,中国位列第5,在发文总量上与德国接近。发达国家在高精度光纤时间频率传递的理论、实验研究以及实际的工程应用起步较早。如从1980年代后期开始,美国就已开始研究设计利用光缆网进行高等级时钟和频率的传递,用于构建NASA的航天测控导航网络,并于2001年率先实现了实际链路的应用,在深空探测领域发挥了巨大的作用;2012年,由欧盟9国(德国、法国、英国、奥地利、意大利、荷兰、瑞典、芬兰、捷克)共同出资合作开展的联合研究项目NEAT-FT正式启动,旨在建设一个频率传输稳定度优于10-17/天,时间同步精度优于100 ps的欧洲时频光纤同步网络[2]。
近3年发文量占比一定程度上反映了某研究领域科研力量近些年的活跃度和发展势头。从近3年发文量占比来看,波兰、中国、捷克和意大利虽在发文总量上落后,但近3年发文量占比较高,均超过美国、日本、法国和德国等国家,展现出强劲的发展势头,说明这些国家在该领域已占有一席之地。
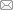
表1给出光纤时间频率传递研究前10国家的主要研究机构发文情况。单从发文量来看,目前位居世界前列的主要研究机构依次为美国国家标准技术研究院(NIST)、日本国家计量院(NMIJ/AIST)、日本电报电话公司(NTT)、法国巴黎天文台(LNE-SYRTE)、德国联邦物理技术研究院(PTB)、英国国家物理实验室(NPL)、美国喷气推进实验室(JPL)、德国马克斯普朗克量子光学研究所(MPQ)、美国天体物理联合实验室(JILA)、波兰克拉科夫理工大学(AGH-UST)、捷克教育科研网络(CESNET)等。上海交通大学、捷克教育科研网络、清华大学和波兰克拉科夫理工大学近3年的发文量占比超过70%,有着很强劲的研究势头。图3进一步描绘了发文10篇以上机构近15年的发展趋势气泡图。
近些年来,在美、日、法、德等国的研究带动下,其他各国的研究小组也都开展了高精度光纤频率传递研究并取得了长足的进步,时间同步的精度由百纳秒级到纳秒级甚至亚纳秒级,传递的距离从几十米到上百千米甚至近千千米,其成果在世界上处于领先水平。如捷克教育科研网联合瑞典国家技术研究所完成了基于双向时间比对方案的744 km和560 km光纤时间传递实验[12];波兰克拉科夫理工大学(AGH-UST)联合法国激光物理实验室完成了基于环回法方案的420 km和540 km光纤时间频率传递实验[13]。国内,2012年清华大学-计量院联合实验小组在往返80 km的商用光纤链路上首次演示了时标脉冲、微波频率的同时传输与同步实验[14];2015年上海交通大学提出一种通过波分复用将基于光学相位噪声补偿的频率传递与基于时分复用的时间传递结合在一起的光纤时间和频率同时传递方案,在100 km的光纤链路上进行了时间和频率同时传递实验[9];2015年中国科学院国家授时中心用线绕光纤进行光频传递实验,在国内首次实现了100 km级的光学频率传递[3]。
3.3.1 基于词频的研究热点分析
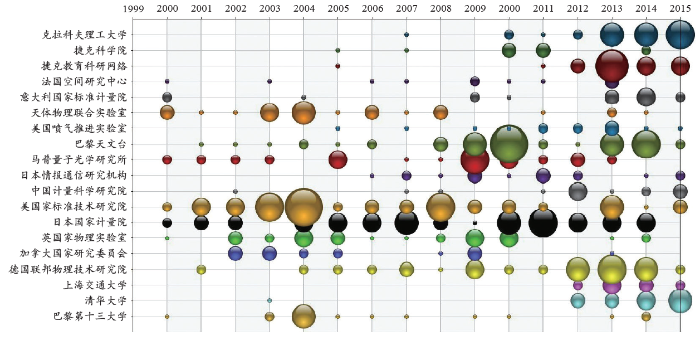
通过TDA文献数据挖掘工具对INSPEC数据库中光纤时间频率传递研究领域的非控制词索引进行清理统计,表2按近3年发文量占比排名前15的非受控词(共涉及文献1 207篇,占文献总量91.4%)列出该领域的研究热点、最相关术语及优势国家。可以看出,近3年发文量占比较高的热点词为“频率传递”、“阿伦方差”、“光纤时间传递”、“单模光纤链路”、“相位噪声”、“光链路”、“光晶格钟”、“掺铒光纤放大器”、“飞秒光频梳”等,此研究热点发文较多的国家主要集中在美国、中国、法国、德国和日本。
3.3.2 主要机构研究热点分析
基于非受控词的词频分析,表3给出光纤时间频率传递领域主要研究机构近期出现的技术热点词。对这些技术热点词进行统计分析,发现目前国际上利用光纤传输高稳时频信号主要集中在光纤微波频率传递、光纤光学频率传递、光纤光学频率梳信号传递技术等方面。
在光纤微波频率传递方面,目前国际上主要包括法国巴黎第十三大学、巴黎天文台、日本通信研究机构、美国家标准技术研究院、捷克教育科研网络、清华大学、加拿大国家研究委员会等利用微波频率级联传输、密集波分复用、双色光程差测定、频谱噪声分布、被动噪声消除等技术方法;在光纤光学频率传递方面,目前国际上主要包括美国家标准技术研究院、美国天体物理联合实验室、法国国家空间研究中心、巴黎天文台、德国联邦物理技术研究院、意大利国家标准计量院等利用相位噪声补偿(多普勒消除技术)、超窄线宽激光、光学频率合成器、量子级联激光器、掺铒光纤放大器、布里渊光纤放大器等技术方法;在光纤光学频率梳信号传递方面,目前国际上主要包括英国国家物理实验室、上海交通大学、波兰克拉科夫理工大学等利用飞秒光学频率梳、中红外量子级联激光频率梳、宽带光学频率梳、传播延迟稳定等技术方法。
通过对光纤时间频率传递相关论文的文献计量学分析发现:光纤时间频率传递领域论文数量整体上呈稳态增长趋势,特别是2000年以后,掀起了利用光纤进行时间频率传递研究的热潮,论文总量增长较快;美国、日本、法国是目前该研究领域论文产出大国,但近几年捷克、中国、波兰和意大利在此研究领域已占有一席之地。主要研究机构中,上海交通大学、捷克教育科研网络、清华大学和波兰克拉科夫理工大学近3年的发文量占比均超过70%,发展势头强劲。基于机构近期出现的技术热点词的统计分析,目前国际上各研究小组利用光纤传输高稳时频信号技术主要集中在光纤微波频率传递、光纤光学频率传递、光纤光学频率梳信号传递等方面。
光纤时间频率传递主题检索策略:
TS=("Atomic clock*" or "Lattice clock*" or "Optical clocks" or "Time and frequency*" or "Frequency transfer*" or "Frequency standard*" or "Frequency metrology" or "Trequency referen*" or "Frequency instabi*" or "Frequency disseminat*" or "Time transfer*" or "Time metrology" or "Time synchron*" or "Time referen*" or "Time interval measurement*" or "Precise time*" or "Accurate time*" or "Ultrastable frequecy*" or "Ultrastable signa*" or "Optical frequency distribution*" or "Optical coherence transfer*" or "Optical frequency comb*" or "optical frequency standard*") AND TS=("Optical link*" or "Optical fibre*" or "Fiber optic link*" or "Optical network*" or "Fiber network*" or "Fiber link*" or "Optical soliton*" or "Satellite links" or "Synchronous Digital Hierarchy" or SDH or "Synchronous Optical Network" or SONET or "Wavelength Division Multiplexing" or DWDM or OTDM or "Telecommunication fiber*" or "Telecommunication link*" or "Fiber dissminat*" or "Single mode* Fiber*" or "spooled fiber*")。
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
| [1] |
DOI:10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2014.34.005
Magsci
URL
[Cite within: 1]
在清华大学与中国计量科学研究院之间往返80 km 的商用光纤链路上进行了时间频率同时传输与同步实验.采用时间频率同时传输与同步的方法,获得了7×10<sup>-15</sup>/s,5×10<sup>-19</sup>/d 的频率传输稳定度结果;通过在发射端主动探测并补偿时间脉冲信号在光纤中传输的时间延迟,实现了±50 ps 的时间同步稳定度指标.鉴于目前基于光纤链路的频率传输方案均受限于点对点传输的问题,设计并完成了可多点下载的频率接收系统,使时间频率传输与同步网络的建设成为可能.
|
| [2] |
DOI:10.7693/wl20140601
URL
[Cite within: 3]
文章介绍了时间频率同步的主要概念及方法。重点介绍了在清华大学与中国计量科学研究院之间往返80 km的商用光纤链路上进行时间频率传输与同步的方案,实验得到7×10-15/s,5×10-19/天的频率传输稳定度和50 fs的时间同步稳定度。针对不同网络结构,文章作者提出了多种光纤同步方案,并着重介绍了时间频率同步在科学研究领域中的一些重要应用。
|
| [3] |
DOI:10.7498/aps.64.120602
Magsci
URL
[Cite within: 2]
随着光钟研究的发展, 光钟的稳定度和不确定度均达到10<sup>-18</sup>量级. 通过光纤可以实现光钟频率信号的高精度传输, 有望用于未来“秒”定义的复现. 演示了百公里级实验室光纤上的光学频率传递. 对于在实验室70 km光纤盘上实现的光频传递, 光纤相位噪声抑制在1-250 Hz傅里叶频率范围内均接近于光纤延时极限, 对应传输稳定度(Allan偏差)为秒级稳定度1.2×10<sup>-15</sup>, 10000 s稳定度为1.4×10<sup>-18</sup>. 实验室100 km光纤的光频传递秒级稳定度也达到了5×10<sup>-15</sup>. 提出了光纤噪声用户端补偿的方案, 可以简化星形传递网络中心站的复杂度. 在25 km光纤上演示了该传递方案, 实现的传输稳定度接近传统前置补偿传递方案.
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-7202.2004.01.001
URL
[Cite within: 1]
分析了物理量测量中时间频率量 的特点 ,主要有 :时间的流逝性 ,时间频率具有最高的测量精密度与准确度 ,时间和频率既密切相关又有区别 ,其计量标准可通过电磁波发播 ,其基准是自然基准 ,其测量精确度与测量时间有关。作者阐述了这些特点对计量技术及建设时间频率系统的影响 ,论述了建设我国独立自主的时间频率系统的必要性及其基本框架 ,从基准、实时、授时、时间频率设备的研制、生产和队伍建设等方面提出了建设的具体设想。
|
| [6] |
DOI:10.1364/OL.36.000511
PMID:21326439
URL
[Cite within: 1]
We demonstrate the transfer of an ultrastable microwave frequency by transmitting a 30-nm-wide optical frequency comb from a mode-locked laser over 8665km of installed optical fiber. The pulse train is returned to the transmitter via the same fiber for compensation of environmentally induced optical path length changes. The fractional transfer stability measured at the remote end reaches 4×10(-17) after 160065s, corresponding to a timing jitter of 6465fs.
|
| [7] |
DOI:10.1007/s00340-012-5241-0
URL
[Cite within: 1]
In this work, we demonstrate for the first time that it is possible to transfer simultaneously an ultra-stable optical frequency and precise and accurate timing over 54002km using a public telecommunication optical fiber network with Internet data. The optical phase is used to carry both the frequency information and the timestamps by modulating a very narrow optical carrier at 1.5502μm with spread spectrum signals using two-way satellite time transfer modems. The results in terms of absolute time accuracy (25002ps) and long-term timing stability (2002ps) well outperform the conventional Global Navigation Satellite System or geostationary transfer methods.
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
DOI:10.3788/aos201535.0406004
URL
[Cite within: 2]
提出了一种基于光纤的时间和频率同时传递方案。采用基于温控光纤延迟线和压电陶瓷(PZT)光纤延迟线的光学相位噪声补偿技术实现高稳定的频率传递。同时,通过波分复用技术在稳定的光纤链路上进行基于时分复用的高精度同纤同波双向时间传递。在100 km的光纤链路上进行了时间和频率同时传递实验,光纤频率传递链路的秒稳定度和天稳定度分别达到5.25×10^-14和1.9×10^-17;双向时间比对在1 s处的时间传递秒稳定度优于40ps,在平均时间1000 s处优于1.5 ps。时间差抖动的峰-峰值和标准差分别小于400 ps和45 ps。
|
| [10] |
DOI:10.1126/science.1218442
PMID:22539714
URL
[Cite within: 1]
Optical clocks show unprecedented accuracy, surpassing that of previously available clock systems by more than one order of magnitude. Precise intercomparisons will enable a variety of experiments, including tests of fundamental quantum physics and cosmology and applications in geodesy and navigation. Well-established, satellite-based techniques for microwave dissemination are not adequate to compare optical clocks. Here, we present phase-stabilized distribution of an optical frequency over 920 kilometers of telecommunication fiber. We used two antiparallel fiber links to determine their fractional frequency instability (modified Allan deviation) to 5 × 10 6115 in a 1-second integration time, reaching 10 6118 in less than 1000 seconds. For long integration times τ, the deviation from the expected frequency value has been constrained to within 4 × 10 6119 . The link may serve as part of a Europe-wide optical frequency dissemination network.
|
| [11] |
DOI:10.1103/PhysRevA.93.033860
URL
[Cite within: 1]
Bidirectional ground-satellite laser links suffer from turbulence-induced scintillation and phase distortion. We study the impact of turbulence on coherent detection and the related phase noise that restricts time and frequency transfer precision. We evaluate the capacity to obtain a two-way cancellation of atmospheric effects despite the asymmetry between up- and downlink that limits the link reciprocity. For ground-satellite links, the asymmetry is induced by point-ahead angle and possibly the use, for the ground terminal, of different transceiver diameters, in reception and emission. The quantitative analysis is obtained thanks to refined end-to-end simulations under realistic turbulence and wind conditions as well as satellite kinematics. These temporally resolved simulations allow characterizing the coherent detection in terms of time series of heterodyne efficiency and phase noise for different system parameters. We show that tip-tilt correction on ground is mandatory at reception for the downlink and as a pre-compensation of the uplink. Besides, thanks to the large tilt angular correlation, the correction is shown to be efficient on uplink despite the point-ahead angle. Very good two-way compensation of turbulent effects is obtained even with the asymmetries. The two-way differential phase noise is reduced to 1 rad, with the best fractional frequency stability below 2 脳10after 1-s averaging time.
|
| [12] |
DOI:10.1109/TIM.2009.2028214
URL
[Cite within: 1]
We have performed time transfer experiments based on passive listening in fiber optical networks using Packet over synchronous optical networking (SONET)/synchronous digital hierarchy (SDH). The experiments have been performed with different complexity and over different distances. For assessment of the results, we have used a GPS link based on carrier-phase observations. On a 560-km link, precision that is relative to the GPS link of <; 1 ns has been obtained over several months. In this paper, we describe and quantify the different error sources influencing the fiber time transfer measurements. We show that the temperature dependence of the optical fiber is the major contribution to the error budget, and, thus, reducing this effect should be the best way of improving the results.
|
| [13] |
DOI:10.1088/0026-1394/50/2/133
URL
[Cite within: 1]
In this paper we present the results of our work concerning the long-distance fibre optic dissemination of time (1 PPS) and frequency (10 MHz) signals generated by atomic sources, such as caesium clocks, hydrogen masers or caesium fountains. For these purposes we developed dedicated hardware (a fibre optic system with active stabilization of the propagation delay and bidirectional fibre optic amplifiers) together with a procedure to enable calibration of the time transfer. Our laboratory measurements performed over fibre lengths of up to 480 km showed an Allan deviation of the order of 4 x 10(-17), time deviation below 1 ps (both at one-day averaging) and the possibility of calibration with picosecond accuracy even for the longest from evaluated links. After successful laboratory evaluation the system was next installed on a 421.4 km long route between the Central Office of Measures (GUM) in Warsaw, Poland, and the Astrogeodynamic Observatory (AOS) in Borowiec near Poznan, Poland. Experiments comparing the UTC(PL) and UTC(AOS) atomic timescales using the fibre optic link and TTS-4 dual-frequency GNSS time transfer receivers showed that the consistency of the results is within the calibration accuracy of the GPS receivers and with much better noise performance. The field operation of the system proved its full functionality and confirmed our previous laboratory evaluation to the maximum extent possible using the methods for comparing distant clocks available at GUM and AOS.
|
| [14] |
DOI:10.1038/srep00556
PMID:22870385
URL
[Cite within: 1]
The synchronisation of time and frequency between remote locations is crucial for many important applications.
|